Power of Edge Computing: Revolutionizing the Tech
In the fast-paced world of technology, edge computing has emerged as a pivotal evolution, shifting data processing from centralized locations to the ‘edge’ of the network closer to where data is generated. This transition is not just about speed; it’s about redefining interactions between data and decisions. This post explores the rise of edge computing, its profound significance, and how it’s sculpting the future of technology.
Table of Contents
Understanding Edge Computing
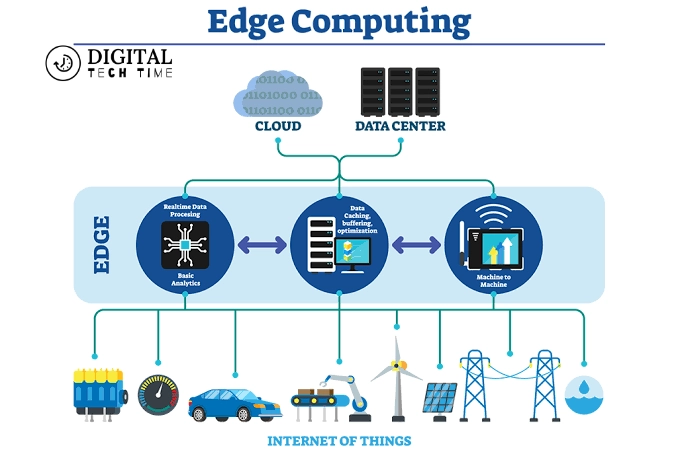
Edge computing is a transformative approach that involves processing data near its source rather than relying on distant cloud data centers. This proximity reduces latency, enhances response times, and saves bandwidth, making operations more efficient and agile.
Key Benefits of Edge Computing:
- Reduced Latency: By minimizing the distance data travels, edge computing significantly reduces response times.
- Bandwidth Savings: Local processing means less data is sent to the cloud, reducing network traffic and associated costs.
- Enhanced Security: Processing data locally can minimize exposure to cyber threats and enhance data privacy.
Benefits of Edge Computing in the Tech Landscape
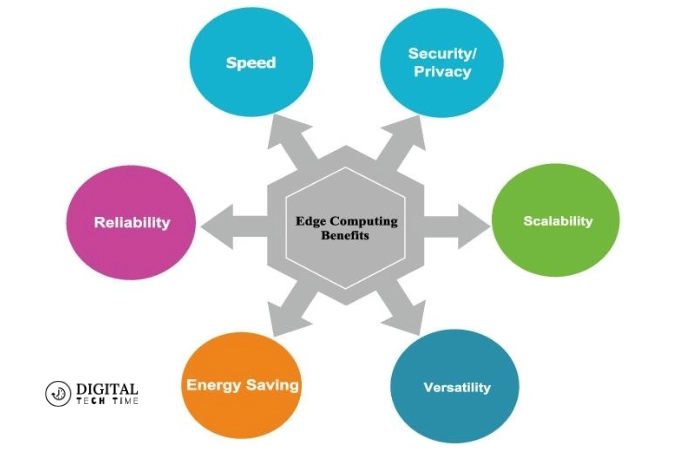
The rise of edge computing is poised to revolutionize the tech landscape, offering many benefits that transcend traditional computing paradigms. Let’s explore some of the critical advantages that edge computing brings to the table:
- Reduced Latency: By processing data closer to the source, edge computing minimizes the need for constant data transmission to centralized servers, significantly reducing latency and enabling real-time decision-making.
- Bandwidth Optimization: With edge computing, only essential data is transmitted to the cloud, reducing the bandwidth requirements and associated costs while ensuring efficient use of network resources.
- Enhanced Data Privacy and Security: By keeping sensitive data local and processing it at the edge, edge computing minimizes the risk of data breaches and enhances data privacy and security.
- Improved Reliability and Resilience: Edge computing architectures are inherently more resilient, as they can continue to operate even in the event of network disruptions or cloud outages, ensuring uninterrupted service delivery.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Edge computing solutions can be easily scaled up or down based on changing requirements, offering flexibility and adaptability to meet evolving business needs.
- Cost Efficiency: By reducing the need for constant data transmission and leveraging local resources, edge computing can lead to significant cost savings, mainly when data volumes are high or network connectivity is limited.
As we embrace the power of edge computing, we unlock a world of possibilities where real-time data processing and analysis become the norm, enabling industries to innovate, optimize, and thrive in the digital age.
The Rise of Edge Computing

The emergence of edge computing is not an isolated phenomenon; instead, it is a convergence of several technological advancements and industry trends that have paved the way for its widespread adoption. Let’s explore the driving forces behind the rise of edge computing:
- The proliferation of IoT Devices: The exponential growth of connected devices, from smart home appliances to industrial sensors, has generated unprecedented data that requires real-time processing and analysis.
- Advancements in Hardware and Computing Power: The development of powerful yet compact computing hardware, such as single-board computers and edge gateways, has enabled the deployment of edge computing solutions in various environments.
- 5G and Low-Latency Networks: The advent of 5G networks and their promise of ultra-low latency and high bandwidth has opened up new possibilities for edge computing, enabling real-time data processing and decision-making.
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: Integrating AI and ML algorithms into edge computing solutions has unlocked new levels of intelligence and automation, allowing for more sophisticated data processing and decision-making at the edge.
- Industry 4.0 and Smart Manufacturing: The drive towards Industry 4.0 and intelligent manufacturing has necessitated deploying edge computing solutions to enable real-time monitoring, control, and optimization of industrial processes.
- Regulatory Compliance and Data Sovereignty: With increasing concerns over data privacy and sovereignty, edge computing provides a solution by keeping sensitive data local and minimizing the need for cross-border data transfers.
Key Players in the Edge Computing Industry
The edge computing revolution has attracted the attention of tech giants and innovative startups alike, each vying to establish a foothold in this rapidly evolving space. Let’s explore some of the key players driving the edge computing industry:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS): AWS, a leading cloud service provider, has embraced edge computing with its AWS Greengrass and AWS Outposts offerings, enabling customers to run AWS services and applications at the edge.
- Microsoft Azure: Microsoft’s Azure IoT Edge and Azure Stack solutions are designed to bring the power of the cloud to the edge, enabling customers to deploy and manage IoT and edge workloads seamlessly.
- Google Cloud Platform: Google’s edge computing offerings, such as Google Cloud IoT Edge and Anthos, empower customers to deploy and manage applications and services at the edge, leveraging Google’s cloud infrastructure.
- NVIDIA: With its powerful GPU technology and edge computing platforms like NVIDIA EGX, the company is enabling advanced AI and machine learning capabilities at the edge, particularly in industries like autonomous vehicles and smart cities.
- Dell Technologies: Dell’s edge computing solutions, including its Dell EMC Integrated Data Protection Appliances and Wyse thin clients, cater to edge computing use cases across multiple industries.
- Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE): HPE’s Edgeline Converged Edge Systems and Aruba Edge Services Platform provide robust edge computing solutions for manufacturing, retail, and telecommunications industries.
- Innovative Startups: The edge computing ecosystem is also fueled by numerous innovative startups, such as FogHorn, Xnor.ai, and Edgeworx, bringing cutting-edge solutions and disruptive technologies to the market.
Challenges and Limitations of Edge Computing
While edge computing offers numerous benefits and promises to revolutionize the tech landscape, it has challenges and limitations. Let’s explore some of the critical considerations and obstacles that need to be addressed:
- Security and Privacy Concerns: With data processing occurring at the edge, there are heightened concerns regarding data security and privacy. Ensuring robust security measures and adhering to data protection regulations are crucial for successfully adopting edge computing solutions.
- Interoperability and Standardization: The need for industry-wide standards and interoperability between edge computing platforms and solutions can hinder seamless integration and deployment across diverse environments.
- Edge Device Management and Maintenance: Managing and maintaining a distributed network of edge devices can be complex and resource-intensive, requiring efficient device management strategies and robust remote monitoring and updating capabilities.
- Power and Resource Constraints: Edge devices often need more power and computational resources, posing challenges in processing power, storage capacity, and battery life, particularly in resource-constrained environments.
- Scalability and Orchestration: As edge computing deployments grow in scale and complexity, ensuring seamless orchestration and coordination between edge devices, gateways, and cloud infrastructure becomes increasingly challenging.
- Skilled Workforce and Training: The successful implementation and maintenance of edge computing solutions require an experienced workforce with expertise in edge computing architectures, edge device management, and edge-specific security protocols.
- Cost and Return on Investment (ROI): While edge computing can offer long-term cost savings, the initial investment in hardware, software, and infrastructure can be substantial, requiring a careful evaluation of the potential return on investment.
Addressing these challenges requires collaborative efforts from industry stakeholders, researchers, and policymakers to develop robust solutions, establish industry standards, and foster a supportive ecosystem for the widespread adoption of edge computing.
Future Trends in Edge Computing

As edge computing continues to gain traction, we can expect to see several exciting trends and developments shaping the future of this transformative technology. Let’s explore some of the key trends that are likely to shape the edge computing landscape:
- Convergence of Edge and Cloud Computing: While edge computing brings processing power closer to the data source, it will not entirely replace cloud computing. Instead, we can expect to see a convergence of edge and cloud computing, with seamless integration and orchestration between the two paradigms, leveraging the strengths of each approach.
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning at the Edge: Integrating AI and ML capabilities will become increasingly prevalent, enabling more intelligent and autonomous decision-making, predictive analytics, and real-time optimization.
- 5G and Beyond: The rollout of 5G networks and the development of future generations of wireless technologies will further enhance the capabilities of edge computing, enabling ultra-low latency, high bandwidth, and seamless connectivity for edge devices and applications.
- Edge-to-Edge Collaboration: As edge computing ecosystems mature, we expect increased collaboration and data sharing between edge devices and networks, enabling more coordinated and intelligent decision-making across various environments.
- Democratization of Edge Computing: With the proliferation of edge computing solutions and the development of open-source platforms, edge computing will become more accessible and affordable, enabling smaller businesses and organizations to leverage its benefits.
- Edge Computing as a Service (ECaaS): Similar to the cloud computing model, we may see the emergence of Edge Computing as a Service (ECaaS) offerings, where edge computing resources and services are provided on a pay-as-you-go or subscription basis, lowering the barriers to entry and enabling greater flexibility.
- Sustainability and Green Computing: As the demand for energy-efficient computing solutions grows, edge computing will play a crucial role in enabling sustainable and eco-friendly data processing, reducing the carbon footprint associated with traditional centralized computing models.
These trends and developments highlight the dynamic and evolving nature of edge computing, showcasing its potential to transform industries and shape the future of computing and data processing.
How to Implement Edge Computing in Your Business
Embracing edge computing in your business can unlock many benefits, from improved operational efficiency and real-time decision-making to enhanced customer experiences and cost savings. However, successfully implementing edge computing requires a strategic approach and careful planning. Here are some critical steps to consider:
- Assess Your Business Needs and Use Cases: Evaluate your business requirements and identify the use cases where edge computing can provide significant value. Consider factors such as real-time data processing needs, latency requirements, and the potential for improved efficiency and cost savings.
- Conduct a Feasibility Study and Cost-Benefit Analysis: Perform a thorough feasibility study to assess the technical and operational requirements for implementing edge computing in your organization. A cost-benefit analysis will also be conducted to evaluate the potential return on investment and justify the investment in edge computing infrastructure.
- Develop an Edge Computing Strategy: Based on your business needs and feasibility assessment, develop a comprehensive edge computing strategy that outlines the architecture, infrastructure, and deployment plan. This strategy should align with your overall business goals and IT roadmap.
- Choose the Right Edge Computing Solutions: Evaluate and select the appropriate edge computing solutions that best fit your requirements. Consider factors such as scalability, security, interoperability, and vendor support. Explore proprietary and open-source options to find the best fit for your organization.
- Implement Edge Computing Infrastructure: Once you have selected the appropriate solutions, implement the edge computing infrastructure. This may involve deploying edge devices, gateways, and edge servers and integrating them with your existing IT infrastructure and cloud services.
- Develop and Deploy Edge Applications and Services: Leverage the edge computing infrastructure to develop and deploy applications and services tailored to your business needs. This may involve leveraging existing software or developing custom applications and services specifically designed for edge computing environments.
- Establish Edge Device Management and Security Protocols: Implement robust device management and security protocols to ensure your edge computing infrastructure’s secure and efficient operation. This includes device provisioning, software updates, and security measures such as encryption and access control.
- Train and Upskill Your Workforce: Invest in training and upskilling your workforce to ensure they have the knowledge and skills to manage and maintain your edge computing infrastructure effectively. This may involve partnering with technology vendors, educational institutions, or specialized training providers.
- Monitor and Optimize Edge Computing Performance: Continuously monitor the performance of your edge computing infrastructure and applications, collecting and analyzing data to identify areas for optimization and improvement. Leverage analytics and machine learning techniques to gain insights and make data-driven decisions.
- Embrace Continuous Innovation and Adaptation: Edge computing is a rapidly evolving field, and it is essential to stay ahead by embracing continuous innovation and adaptation. Stay informed about emerging trends, technologies, and best practices, and be prepared to adapt your edge computing strategy as needed to maintain a competitive edge.
Read Also: Future of Technology With Google Cloud AI
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is edge computing?
Edge computing optimizes cloud computing systems by processing data at the network’s edge near the source.
How does edge computing enhance data security?
By processing data locally, edge computing minimizes the distance data travels, reducing the exposure to potential cyber threats.
Can edge computing operate independently of the cloud?
While it enhances cloud operations, edge computing can handle many operations independently, providing flexibility and resilience.
Conclusion
The rise of edge computing marks a significant milestone in the evolution of technology. Bringing data processing closer to the source offers unprecedented speed and efficiency, transforming industries and setting new standards for digital innovation. As we embrace this shift, the potential for what we can achieve with edge computing is only limited by our imagination.