The Rising Threat: After WannaCry Ransomware Fireball Malware Spreads to Infect 250 Million Computers
After WannaCry Ransomware Fireball Malware annihilated hundreds of thousands of computers all around the world, we are witnessing the rise of another dangerous malware campaign named Fireball. Security firm Check Point Threat Intelligence discovered this high volume threat which has infected more than 250 million computers worldwide.
Table of Contents
The Aftermath of the WannaCry Ransomware Fireball Malware
The WannaCry ransomware attack, which struck in May 2017, was a stark reminder of the devastating impact cyber threats can have on individuals, businesses, and even entire nations. The malware spread rapidly, encrypting files and demanding ransom payments for the decryption keys. The attack caused widespread disruption, affecting hospitals, businesses, and government agencies worldwide.
The aftermath of the WannaCry attack left many organizations and individuals shaken, underscoring the urgent need for robust cybersecurity measures and increased vigilance against emerging threats. Within this context, the Fireball malware has emerged, posing a new and formidable challenge to the global cybersecurity landscape.
Understanding the Fireball Malware

Fireball is a malware first discovered 2016 by security researchers at Check Point Software Technologies. The malware is primarily designed to hijack web browsers and redirect users to malicious websites, often to generate fraudulent advertising revenue.
Fireball’s primary mode of infection is through bundled software, which is often packaged with seemingly legitimate programs or applications. Once installed on a victim’s computer, Fireball can take control of the user’s web browser, modify the default search engine and homepage, and redirect the user to various websites, many of which are designed to generate fraudulent advertising revenue.
How Fireball Infects Computers

The Fireball malware typically spreads through bundled software with other applications or programs that users may download and install. This can include free software, cracked or pirated programs, and even some legitimate applications that the malware has compromised.
Once installed, Fireball can silently infiltrate the victim’s computer, often undetected by traditional antivirus software. The malware then sets its primary objective: hijacking the user’s web browser and redirecting them to a network of malicious websites.
Fireball’s Impact on Infected Computers
The consequences of Fireball’s infection can be far-reaching and damaging. Beyond the apparent inconvenience of hijacking one’s web browsing experience, the malware can pose a significant security risk to the infected computer.
Fireball can collect sensitive user data, such as browsing history, login credentials, and personal information. This data can then be transmitted to the malware’s command-and-control servers, potentially leading to identity theft, financial fraud, and other malicious activities.
Additionally, Fireball can be used as a platform to deliver additional malware payloads, further compromising the infected system and exposing the user to even more significant threats.
Fireball’s Global Reach – Infecting 250 Million Computers
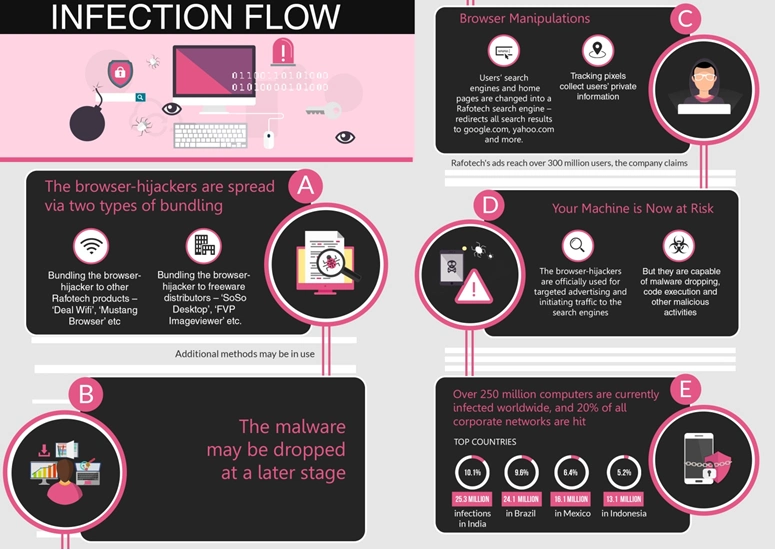
The Fireball malware has been described as one of the most widespread malware infections in recent history, with an estimated 250 million computers worldwide affected. This staggering figure highlights the sheer scale and pervasiveness of this threat.
The malware’s global reach is a testament to its sophisticated distribution methods and the ease with which it can be bundled with other software. Fireball has been detected in over 20 countries, with most infections occurring in China, India, and the United States.
Fireball’s Key Features and Capabilities
Fireball is a highly sophisticated malware with a range of advanced features and capabilities that make it a formidable threat:
- Browser Hijacking: Fireball’s primary function is to take control of the user’s web browser, modify the default search engine and homepage, and redirect the user to a network of malicious websites.
- Data Collection: The malware can collect sensitive user data, such as browsing history, login credentials, and personal information, which can then be transmitted to the malware’s command-and-control servers.
- Payload Delivery: Fireball can deliver additional malware payloads, further compromising the infected system and exposing users to even more significant threats.
- Persistence: Fireball is designed to maintain a persistent presence on the infected system, ensuring it continues operating even after system reboots or other attempts to remove it.
- Evasion Tactics: The malware employs various techniques to evade detection by traditional antivirus software, making it challenging to identify and remove.
Steps to Protect Your Computer from Fireball

In the face of this growing threat, it is essential to take proactive measures to protect your computer and your organization from the Fireball malware. Here are some critical steps you can take:
- Keep Your Software Up-to-Date: Ensure that your operating system, web browsers, and other software are regularly updated with the latest security patches and fixes.
- Use Reputable Antivirus Software: Install a reliable antivirus or anti-malware solution and keep it up-to-date to help detect and prevent Fireball infections.
- Be Cautious with Downloads: Exercise caution when downloading and installing software from the internet, especially from unfamiliar or untrusted sources.
- Enable Browser Security Features: Configure your web browser’s security settings to block suspicious downloads and prevent unwanted redirects.
- Educate Employees: Provide cybersecurity awareness training to your employees, teaching them to recognize and avoid potential Fireball infection vectors.
Fireball Removal and Detection Tools
If you suspect that the Fireball malware has infected your computer, there are several tools and resources available to help you detect and remove the threat:
- Malwarebytes: Malwarebytes is a popular anti-malware solution that can detect and remove Fireball and other types of malware.
- AdwCleaner: AdwCleaner is a free tool specializing in detecting and removing adware, potentially unwanted programs (PUPs), and other types of malware, including Fireball.
- Emsisoft Emergency Kit: The Emsisoft Emergency Kit is a portable, bootable antivirus tool that can scan and clean infected systems, including those affected by Fireball.
- Kaspersky Virus Removal Tool: Kaspersky’s free Virus Removal Tool can detect and remove Fireball and other types of malware from your computer.
Related Post: Cybersecurity or Digital Marketing: Choosing the Right Career Path
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is the Fireball malware?
A: Fireball is a malware that hijacks web browsers and redirects users to malicious websites, often to generate fraudulent advertising revenue. It has infected an estimated 250 million computers globally.
Q: How does Fireball infect computers?
A: Fireball spreads through bundled software, packaged with other applications or programs that users may download and install.
Q: What are the consequences of a Fireball infection?
A: Fireball can collect sensitive user data, such as browsing history and login credentials, and can be used to deliver additional malware payloads, further compromising the infected system.
Q: How can I protect my computer from Fireball?
A: Keep your software up-to-date, use reputable antivirus software, be cautious with downloads, enable browser security features, and educate your employees about the threat.
Q: How can I remove Fireball from my computer?
A: You can use tools like Malwarebytes, AdwCleaner, Emsisoft Emergency Kit, and Kaspersky Virus Removal Tool to detect and remove the Fireball malware.
Conclusion
In this research we’ve described Rafotech’s browser-hijackers operation – possibly the largest infection operation in history. We believe that although this is not a typical malware attack campaign, it has the potential to cause irreversible damage to its victims as well as worldwide internet users, and therefore it must be blocked by security companies.
The full distribution of Fireball is not yet known, but it is clear that it presents a great threat to the global cyber ecosystem. With a quarter billion infected machines and a grip in one of every five corporate networks, Rafotech’s activities make it an immense threat.