10 Benefits of Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare
In the ever-evolving landscape of modern healthcare, the integration of Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare has emerged as a transformative force, reshaping how we approach medical care. As we stand at the precipice of a technological revolution, it’s imperative to understand the profound impact AI is poised to have on our well-being. In this comprehensive article, we will delve into AI’s remarkable benefits to the healthcare industry, unveiling a future where precision, efficiency, and personalized care become the new standard.
AI, with its ability to process vast amounts of data, recognize patterns, and make informed decisions, has the potential to revolutionize every aspect of healthcare. From early disease detection to streamlined medical research, AI is paving the way for a more proactive and tailored approach to patient care. As we explore these ten incredible benefits, we will uncover how AI transforms the healthcare landscape, empowers medical professionals, and ultimately improves patient outcomes.
Table of Contents
How Artificial Intelligence is Revolutionizing the Healthcare Industry

The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) into the healthcare industry has ushered in a new era of innovation and transformation. This cutting-edge technology is revolutionizing how we approach medical care, offering unprecedented opportunities to enhance patient outcomes, streamline processes, and unlock new frontiers in medical research.
AI’s ability to analyze vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and make informed decisions is at the heart of this revolution. By harnessing the power of machine learning algorithms and advanced computational capabilities, AI empowers healthcare professionals with powerful tools to improve diagnosis, treatment, and overall patient care.
One of AI’s most significant impacts in healthcare is its potential to augment human expertise. Through AI-powered decision support systems, medical professionals can access real-time insights and recommendations based on the analysis of patient data, medical literature, and best practices. This collaboration between human expertise and AI-driven intelligence is paving the way for more accurate diagnoses, personalized treatment plans, and improved patient outcomes.
Benefit 1: Improved Diagnosis and Treatment

Accurate and timely diagnosis is paramount to ensuring effective treatment and positive patient outcomes. Artificial Intelligence (AI) has emerged as a game-changer in this domain, offering unprecedented capabilities to enhance diagnostic accuracy and streamline treatment processes.
- Accurate and Timely Diagnosis: AI enhances diagnostic accuracy and streamlines treatment processes.
- Data Analysis: AI can analyze vast amounts of medical data, identifying patterns and nuances that human experts often miss.
- Image Analysis: AI-powered systems detect minute irregularities in medical scans (e.g., MRIs, X-rays) with high accuracy, aiding in early disease detection and reducing misdiagnosis risks.
- Decision Support: AI-driven systems provide real-time recommendations based on a patient’s medical history and symptoms, aiding physicians in making informed decisions.
- Personalized Medicine: AI enables customized treatment strategies by analyzing a patient’s genetic makeup and lifestyle factors, improving treatment efficacy and minimizing adverse reactions.
- Overall Impact: AI in diagnosis and treatment leads to more precise, efficient, and personalized healthcare, improving patient outcomes and quality of life worldwide.
Benefit 2: Enhanced Patient Care and Experience

Artificial Intelligence (AI) has emerged as a powerful ally in enhancing patient care and elevating the overall patient experience in the ever-evolving healthcare landscape. By leveraging advanced technologies and data-driven insights, AI is revolutionizing how healthcare services are delivered, ensuring a more personalized, efficient, and compassionate approach to patient care.
1. Data Privacy and Security
- Sensitive Information: AI systems rely on vast amounts of sensitive personal data, including medical records, genetic information, and lifestyle details. Ensuring the privacy and security of this data is paramount to prevent unauthorized access and potential misuse.
- Data Breaches: The risk of data breaches increases with the centralization of data in AI systems. Robust encryption, secure data storage, and stringent access controls are essential to safeguard patient information.
2. Informed Consent
- Transparency: Patients must be fully informed about how AI systems use their data. This includes understanding the scope of data collection, the purpose of its use, and the potential risks involved.
- Autonomy: It is critical to respect patient autonomy by obtaining explicit consent for data usage. Patients should have the right to opt out of AI-driven processes without compromising their access to healthcare services.
3. Bias and Fairness
- Algorithmic Bias: AI systems that are trained on unrepresentative data sets can inadvertently perpetuate existing biases in healthcare. This can lead to disparities in diagnosis and treatment across different demographic groups.
- Fair Access: Ensuring that AI technologies are accessible to all patients, regardless of socioeconomic status, is essential to avoid widening the gap in healthcare equity.
4. Accountability and Transparency
- Decision-Making: It is crucial to maintain transparency in AI decision-making processes. Healthcare providers must understand how AI systems arrive at their conclusions to ensure they can explain and justify these decisions to patients.
- Responsibility: Clear guidelines are needed to delineate the responsibility between AI systems and human healthcare providers. In case of errors, it must be clear who is accountable.
5. Ethical Use of AI
- Purpose Limitation: AI should be used strictly for the purposes it was designed, not for unrelated activities that could compromise patient trust.
- Human Oversight: Despite the advanced capabilities of AI, human oversight remains essential. Healthcare professionals should always have the final say in patient care decisions, using AI as a support tool rather than a replacement.
6. Impact on Employment
- Job Displacement: Integrating AI in healthcare could lead to job displacement for specific roles. Ethical considerations must include strategies for retraining and redeploying affected healthcare workers.
- Collaboration: Fostering a collaborative environment where AI augments human capabilities rather than replaces them is crucial for ethical integration.
7. Regulatory Compliance
- Legal Frameworks: Adherence to legal and regulatory frameworks governing the use of AI in healthcare is essential. This includes compliance with data protection laws like GDPR and healthcare regulations like HIPAA.
- Ongoing Monitoring: The continuous monitoring and updating of AI systems must ensure they comply with evolving legal and ethical standards.
- By addressing these ethical considerations and privacy concerns, we can harness the potential of AI in patient care while safeguarding patient rights and fostering trust in these advanced technologies.
Benefit 3: Efficient Administrative Tasks

- Automation of Repetitive Tasks: AI automates scheduling appointments, managing medical records, processing insurance claims, and handling billing inquiries, speeding up these processes and freeing human resources for critical patient care.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): AI-driven NLP technologies manage and analyze vast amounts of unstructured data, such as physician notes and patient histories, extracting valuable insights and improving data management for informed decision-making.
- Predictive Analytics: AI helps in resource allocation and supply chain management by analyzing historical data and forecasting future demand, optimizing inventory levels, minimizing waste, and ensuring the timely availability of medical supplies.
- Cybersecurity: AI-powered cybersecurity solutions detect and mitigate potential cyber threats, protecting sensitive patient data and ensuring compliance with regulations, thereby maintaining the integrity and confidentiality of patient information.
- Overall Impact: AI in administrative tasks streamlines operations, reduces costs, and enhances efficiency, allowing healthcare professionals to focus more on delivering exceptional patient care and improving patient outcomes.
Benefit 4: Early Disease Detection and Prevention
- Advanced Data Analysis: AI analyzes vast amounts of medical data, including patient records, medical images, and genomic information, to identify patterns and nuances that may indicate the presence of a disease before symptoms appear.
- Accurate Image Analysis: AI-powered systems detect minute irregularities in medical scans (e.g., MRIs, X-rays) with high accuracy, facilitating early detection of conditions like cancer and timely intervention and successful treatment.
- Predictive Analytics: AI helps healthcare providers identify individuals at higher risk for developing certain diseases by analyzing medical history, lifestyle factors, and genetic predispositions, providing personalized recommendations for preventive measures.
- Genomics and Precision Medicine: AI in genomics allows analysis of an individual’s genetic makeup to identify potential genetic markers associated with specific diseases, enabling personalized prevention strategies and targeted treatments.
- Virtual Health Assistants: AI-powered virtual assistants and chatbots provide reliable health information, answer common medical queries, encourage healthier lifestyles, and prompt timely medical attention, aiding disease prevention.
- Proactive and Personalized Healthcare: By leveraging AI for early disease detection and prevention, healthcare can become more proactive and personalized, empowering individuals to take control of their well-being and reducing the overall burden on healthcare systems.
Benefit 5: Personalized Medicine
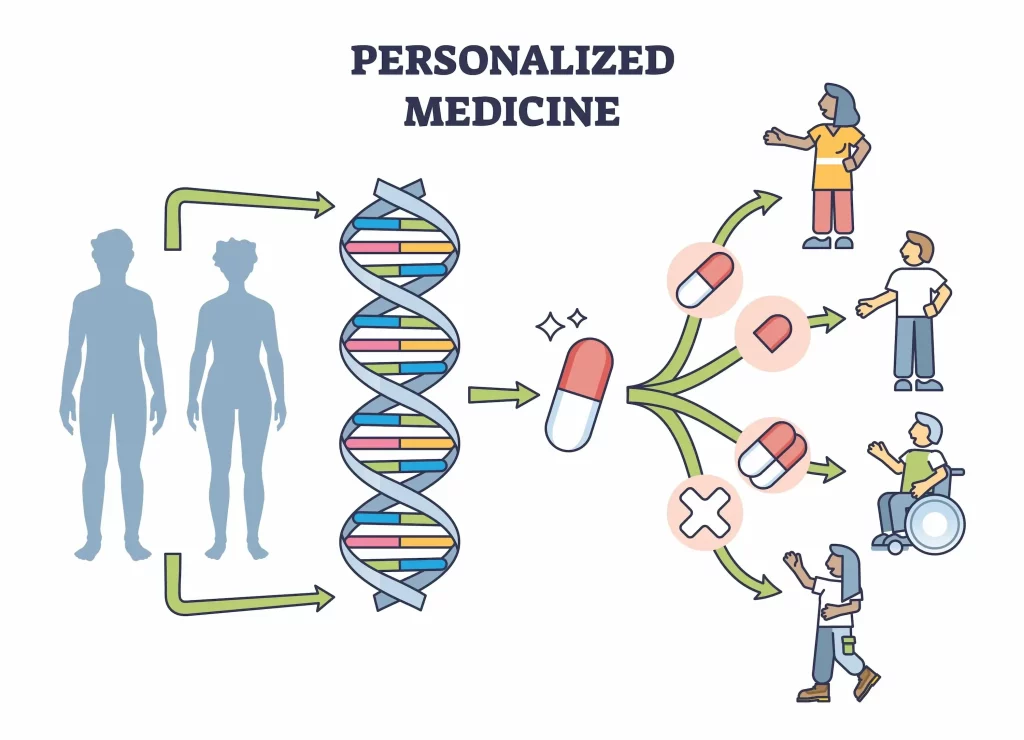
1. Data Privacy and Security
- Sensitive Information: Personalized medicine relies heavily on genetic, medical, and lifestyle data, which are highly sensitive. Ensuring the privacy and security of this data is critical to prevent unauthorized access and protect patient confidentiality.
- Data Breaches: As the volume of data grows, so does the risk of breaches. Implementing robust encryption, secure data storage, and stringent access controls is essential to safeguard patient information.
2. Data Integration and Interoperability
- Diverse Data Sources: Integrating data from various sources (e.g., genetic information, electronic health records, lifestyle data) is complex. Ensuring interoperability among different systems and data formats is a significant challenge.
- Standardization: Lack of standardized data formats and protocols can hinder the seamless integration and analysis of diverse datasets, affecting the accuracy and reliability of personalized medicine insights.
3. Ethical and Legal Issues
- Informed Consent: Patients must be fully informed about how their data will be used in personalized medicine. Obtaining explicit consent and ensuring transparency in data usage is crucial to maintaining trust.
- Discrimination and Bias: There is a risk of genetic discrimination by employers or insurers based on genetic information. Legal frameworks need to evolve to protect individuals from such biases.
4. Technical and Computational Challenges
- Complex Algorithms: It is technically challenging to develop and validate complex machine learning algorithms that can accurately analyze vast and diverse datasets.
- Computational Power: Personalized medicine requires significant computational resources to process and analyze large volumes of data, which can be a constraint for many healthcare institutions.
5. Cost and Accessibility
- High Costs: Implementing personalized medicine can be expensive, involving advanced diagnostic tools, genetic testing, and sophisticated AI systems. This can limit accessibility, particularly in low-resource settings.
- Insurance Coverage: The extent to which personalized medicine procedures and treatments are covered by insurance can impact their accessibility and adoption.
6. Clinical Validation and Adoption
- Evidence-Based Validation: Personalized medicine approaches need rigorous clinical validation to ensure their efficacy and safety. Gathering sufficient evidence can be time-consuming and resource-intensive.
- Adoption by Healthcare Providers: Integrating personalized medicine into routine clinical practice requires training and buy-in from healthcare providers, who may resist adopting new technologies and methodologies.
7. Patient Engagement and Education
- Understanding and Acceptance: Patients need to understand the benefits and limitations of personalized medicine. Effective communication and education are essential to ensure patient engagement and acceptance.
- Managing Expectations: It is crucial to set realistic expectations about the outcomes and benefits of personalized medicine to avoid disappointment and maintain trust.
8. Regulatory and Policy Challenges
- Regulatory Frameworks: Existing regulatory frameworks may need to be fully equipped to address the complexities of personalized medicine. Developing new guidelines and policies is necessary to ensure ethical and safe practices.
- Global Variations: Regulatory and policy environments vary across countries, creating challenges for the worldwide implementation and standardization of personalized medicine.
Benefit 6: Streamlined Medical Research and Development

- Data Analysis: AI can analyze vast amounts of data, including scientific literature, clinical trial data, and genomic information, identifying patterns and generating hypotheses that human researchers might miss.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): AI-powered NLP technologies rapidly analyze and synthesize large volumes of scientific literature, helping researchers stay current with developments and uncover new areas for exploration.
- Clinical Trials: AI improves clinical trials by enabling efficient patient recruitment, optimizing trial designs, and monitoring outcomes, leading to more accurate and reliable results.
- Drug Development: AI facilitates virtual screening and molecular modeling to identify potential drug candidates and predict their interactions with biological targets, accelerating drug development.
- Robotic Systems: AI-powered robotic systems automate repetitive laboratory tasks, enabling high-throughput experimentation increasing efficiency, accuracy, and reproducibility while minimizing human error.
- Overall Impact: AI in medical research and development accelerates scientific discoveries, fosters innovation, and leads to more effective treatments, ultimately improving patient outcomes and advancing human health and well-being.
Benefit 7: Cost Reduction in Healthcare
1. Data Privacy and Security
- Sensitive Data: AI systems in healthcare handle susceptible patient data, including medical records, genetic information, and personal details. Ensuring robust data privacy and security measures is crucial to prevent breaches and unauthorized access.
- Compliance: Adhering to HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) regulations in the US, GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) in Europe, and other regional laws is essential to safeguard patient information.
2. Data Quality and Standardization
- Data Integrity: AI systems require high-quality, accurate, and standardized data. Inconsistent, incomplete, or erroneous data can lead to inaccurate predictions and recommendations.
- Interoperability: Integrating data from various sources, such as electronic health records (EHRs), medical imaging, and lab results, requires interoperability standards that must often be improved.
3. Bias and Fairness
- Algorithmic Bias: AI algorithms can inherit biases in training data, leading to unfair or discriminatory outcomes. This can be particularly problematic in healthcare, where biased algorithms could affect diagnosis and treatment.
- Equity: Ensuring AI systems provide equitable healthcare across different demographic groups is a significant challenge, requiring ongoing algorithm monitoring and adjustments.
4. Clinical Validation and Accuracy
- Validation: AI systems must undergo rigorous clinical validation to ensure their safety, accuracy, and efficacy. This process can be time-consuming and resource-intensive.
- Reliability: Ensuring AI systems consistently deliver accurate and reliable results in diverse clinical settings is critical to gaining the trust of healthcare professionals and patients.
5. Ethical and Legal Issues
- Informed Consent: Patients must be informed about how AI will be used in their care and provide consent. Ensuring transparency and understanding is essential.
- Liability: Determining liability in cases where AI systems make errors or contribute to adverse outcomes is complex. Legal frameworks need to evolve to address these issues.
6. Integration into Clinical Workflows
- Adoption: Integrating AI into existing clinical workflows can be challenging. Healthcare professionals may only accept new technologies if they perceive them as disruptive or time-consuming.
- Training: Adequate training and support are necessary to ensure healthcare providers can effectively use AI systems. This includes understanding how to interpret AI-generated recommendations and insights.
7. Cost and Accessibility
- Implementation Costs: Developing, deploying, and maintaining AI systems can be expensive. Ensuring these technologies are accessible to low-resource settings is a significant challenge.
- Healthcare Disparities: If its benefits are not equitably distributed, AI could exacerbate existing healthcare disparities.
8. Transparency and Explainability
- Black Box Problem: Many AI systems, particularly those based on deep learning, operate as “black boxes,” making it difficult to understand how they arrive at specific conclusions. This lack of transparency can hinder trust and acceptance.
- Explainability: Providing clear and understandable explanations for AI-driven decisions is essential for healthcare providers and patients to trust and effectively use these systems.
9. Continuous Monitoring and Updating
- Dynamic Environment: Healthcare is a dynamic field with constantly evolving knowledge and practices. AI systems need continuous monitoring, updating, and retraining to stay current and practical.
- Adaptability: It is crucial for AI systems’ long-term viability to be able to adapt to new data, medical guidelines, and technologies.
Benefit 8: Real-Time Monitoring and Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics in healthcare leverages advanced technologies and vast amounts of data to improve patient outcomes, operational efficiency, and overall healthcare delivery. Here are some concrete examples of how predictive analytics is being used in the healthcare sector:
1. Predicting COVID-19 Patient Outcomes
- Application: Machine learning models have been used to forecast the clinical severity of COVID-19 in patients based on data gathered within the first 24 hours of hospitalization.
- Outcome: These models have shown high accuracy in predicting the intensity of sickness, helping healthcare providers intervene more effectively and allocate resources appropriately.
2. Reducing Hospital Readmissions
- Case Study: Using predictive analytics, UnityPoint Health reduced hospital readmissions by 40% over 18 months.
- Method: By analyzing patient symptoms and predicting the likelihood of their return, physicians could proactively adjust treatment plans, preventing rehospitalization.
3. Improving Chronic Disease Management
- Application: Predictive models identify high-risk patients for chronic diseases such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and kidney disease.
- Outcome: This allows for early interventions and personalized treatment plans, which help manage and prevent the progression of chronic conditions, ultimately reducing healthcare costs and improving patient quality of life.
4. Enhancing Remote Patient Monitoring
- Technology: AI-powered wearable devices and telemedicine platforms enable continuous health monitoring.
- Benefit: Real-time data from these devices allows for timely interventions and personalized care recommendations, reducing the need for frequent hospital visits and improving patient outcomes.
5. Forecasting Equipment Maintenance Needs
- Application: Predictive maintenance systems analyze data from medical devices to predict potential failures or maintenance needs.
- Outcome: This proactive approach minimizes downtime, ensures uninterrupted patient care, and reduces long-term costs associated with equipment repairs and replacements.
6. Optimizing Resource Allocation and Staffing
- Example: The Gundersen Health System used predictive analytics to increase room utilization by 9%.
- Benefit: By predicting patient flow and staffing needs, healthcare providers can optimize resource allocation, reduce staff burnout, and ensure maximum operational efficiency.
7. Identifying At-Risk Patients
- Application: Predictive models can identify patients at higher risk of hospitalization based on factors like age, chronic illnesses, and medication adherence.
- Outcome: Early identification allows healthcare providers to offer timely interventions, reducing the likelihood of severe health issues and hospitalizations.
8. Disease Prevention and Early Detection
- Benefit: Predictive analytics can detect early symptoms of diseases, enabling preventive care before the onset of severe symptoms that require more expensive treatments.
- Example: Identifying early signs of cardiovascular disease or diabetes allows for early intervention and better management of these conditions.
9. Population Health Management
- Application: Predictive analytics can manage population health by identifying cohorts exposed to possible disease outbreaks and initiating preventive measures.
- Outcome: This leads to improved population health and reduced healthcare costs.
Benefit 9: Automating Repetitive Tasks

1. Streamlining Administrative Processes
- Tasks: Scheduling appointments, managing medical records, processing insurance claims, handling billing inquiries.
- Benefits: Speed, accuracy, reduced human error, improved operational efficiency.
2. Enhancing Data Management with NLP
- Technologies: AI-driven natural language processing (NLP).
- Applications: Analyzing unstructured data like physician notes, patient histories, and medical literature.
- Benefits: Extracting valuable insights, identifying patterns, informed decision-making, and enhanced patient care.
3. Automating Laboratory Workflows and Clinical Research
- Technologies: AI-powered robotic systems.
- Tasks: Sample preparation, data entry, experimental setup.
- Benefits: High-throughput experimentation, minimized human error, reliable and reproducible results, accelerated scientific discoveries and treatment development.
4. Transforming Healthcare Delivery with Virtual Assistants and Chatbots
- Technologies: AI-driven virtual assistants and chatbots.
- Applications: Providing personalized guidance, answering common medical queries, and assisting with routine tasks.
- Benefits: Freeing healthcare professionals to focus on complex and critical patient care aspects, especially in resource-limited settings.
Overall Impact
- Operational Efficiency: Enhanced through automation of repetitive tasks.
- Cost Reduction: Lower operational costs due to increased efficiency.
- Empowerment of Healthcare Professionals: Allowing them to focus on delivering exceptional patient care and driving innovation.
By integrating AI to automate repetitive tasks, healthcare can significantly improve efficiency, reduce costs, and improve overall quality of care.
Benefit 10: Improved Patient Data Security and Privacy

1. Real-Time Threat Detection and Mitigation
- Capabilities: Continuous monitoring of network traffic, identifying anomalies, and responding to potential threats.
- Technologies: AI-powered security systems, machine learning algorithms, advanced analytics.
- Benefits: Proactive and dynamic defense against cyber threats, reduced risk of data breaches.
2. Enhanced Access Control and Authentication
- Technologies: AI-driven access control, biometric authentication (facial recognition, fingerprint scanning).
- Benefits: Robust identity verification, restricted access to sensitive medical information, reduced risk of unauthorized access.
3. Advanced Data Encryption and Privacy-Preserving Technologies
- Technologies: AI-powered encryption algorithms, differential privacy, secure multi-party computation.
- Benefits: Robust protection for patient data, secure data analysis and sharing, and maintaining confidentiality even in case of breaches.
4. AI-Powered Auditing and Compliance Tools
- Technologies: Continuous monitoring of data access and usage patterns.
- Compliance: Adherence to regulations like HIPAA and GDPR.
- Benefits: Identify potential compliance violations proactively to avoid fines and legal consequences.
Overall Impact
- Data Security: Enhanced protection of patient data and privacy.
- Trust and Confidence: Fostering trust in the healthcare system by ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of medical information.
- Empowerment: Enabling individuals to take an active role in their healthcare journey and be secure in knowing their personal information is protected.
Leveraging AI for improved patient data security and privacy can help healthcare organizations ensure robust data protection, regulatory compliance, and enhanced patient trust.
Related Post: Future of Technology With Google Cloud AI
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How does AI improve healthcare?
AI can revolutionize healthcare by enhancing diagnosis and treatment accuracy, enabling early disease detection, personalizing medicine, streamlining medical research, reducing costs, automating repetitive tasks, and improving patient data security and privacy.
Is AI a threat to healthcare professionals?
AI is not a threat but a powerful tool to augment and support healthcare professionals. AI systems are designed to assist and complement human expertise, not replace it entirely.
How is patient privacy protected with AI?
AI-powered security systems, such as advanced encryption algorithms, biometric authentication, and privacy-preserving techniques, can safeguard patient data and ensure compliance with strict privacy regulations.
Can AI replace human doctors?
While AI can assist in various aspects of healthcare, such as diagnosis and treatment recommendations, it is unlikely to replace human doctors in the foreseeable future. The human touch, empathy, and complex decision-making abilities of healthcare professionals are still invaluable.
How can AI personalize medicine?
AI can analyze vast amounts of data, including genetic information, medical histories, and lifestyle factors, to develop personalized treatment plans tailored to each individual’s unique characteristics and needs.
Is AI expensive to implement in healthcare?
While the initial investment in AI technology and infrastructure can be substantial, the long-term cost savings and efficiency gains achieved through AI can offset these expenses and provide a significant return on investment.
How can AI improve patient care and experience?
AI can enhance patient care and experience by streamlining communication, providing personalized guidance, enabling remote monitoring, and optimizing resource allocation for smoother patient flow and reduced wait times.
How is AI used in medical research and drug development?
AI can analyze vast amounts of scientific data, identify potential drug candidates, optimize clinical trial designs, and accelerate drug development, leading to faster discoveries and more effective treatments.
What are the challenges of implementing AI in healthcare?
Some challenges include data quality and availability, ethical considerations, regulatory compliance, and the need for continuous training and updating of AI systems to ensure accuracy and reliability.
How can healthcare organizations prepare for the adoption of AI?
Organizations can prepare by investing in data infrastructure, fostering collaboration between healthcare professionals and AI experts, providing training and education, and establishing clear ethical guidelines and governance frameworks for AI implementation.
Conclusion
Integrating Artificial Intelligence (AI) in healthcare marks the dawn of a transformative era. AI’s capabilities in enhancing diagnosis accuracy, enabling early disease detection, and personalizing treatment are redefining healthcare delivery. By leveraging advanced algorithms and data-driven insights, healthcare professionals can make more informed decisions, optimize resources, and provide exceptional patient care.
AI accelerates medical research and drug development, paving the way for groundbreaking advancements and faster access to life-saving treatments. With applications ranging from real-time monitoring and predictive analytics to automating repetitive tasks and enhancing data security, AI is poised to revolutionize every facet of healthcare.