How to Prepare for Cyber Attack on Power Grid
In the contemporary, heavily interconnected world, a power grid forms a vital base of our sophisticated lifestyle. However, our increasing reliance upon technology exposes the critical system to growing cyber-attack risks. Potential consequences of a successful cyber attack on the power grid range from widespread blackouts to cascading failures that can bring about the collapse of an entire region.
As custodians of this critical infrastructure, we must be consistently vigilant and further aggressive in defending the grid against cyber threats. This paper provides a comprehensive guide on preparing for and mitigating the impact of a cyber attack on the power grid.
Table of Contents
Understanding the Potential Impact of a Cyber Attack on the Power Grid
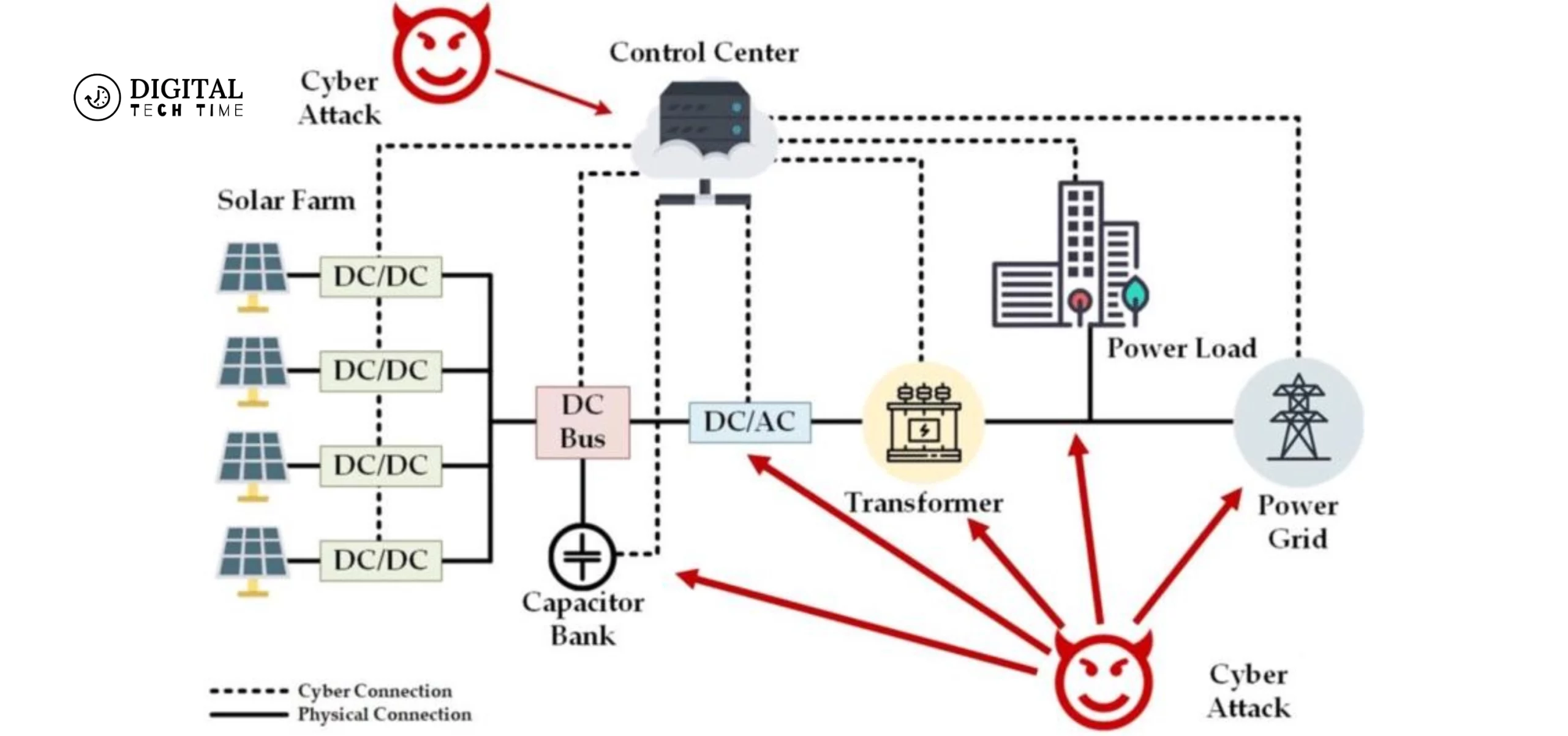
A cyber attack on the power grid can manifest in various forms, each with unique consequences. Some potential impacts include:
- Widespread power outages: A successful cyber attack could disrupt the flow of electricity, leading to widespread blackouts that affect homes, businesses, and critical infrastructure such as hospitals and communication networks.
- Physical damage to the equipment: Malicious actors may attempt to gain control over industrial control systems (ICS), and issue commands that cause physical damage to power generation and transmission equipment, potentially leading to prolonged outages and costly repairs.
- Economic disruption: A prolonged power outage can have far-reaching economic implications, impacting businesses, supply chains, and financial markets, resulting in significant financial losses.
- Cascading failures: The interconnected nature of the power grid means that a localized cyber attack could potentially trigger cascading failures, leading to widespread outages across multiple regions or even countries.
To effectively prepare for and mitigate these potential impacts, we must adopt a comprehensive approach that addresses both technical and operational aspects of cyber security.
Assessing the Vulnerabilities of the Power Grid
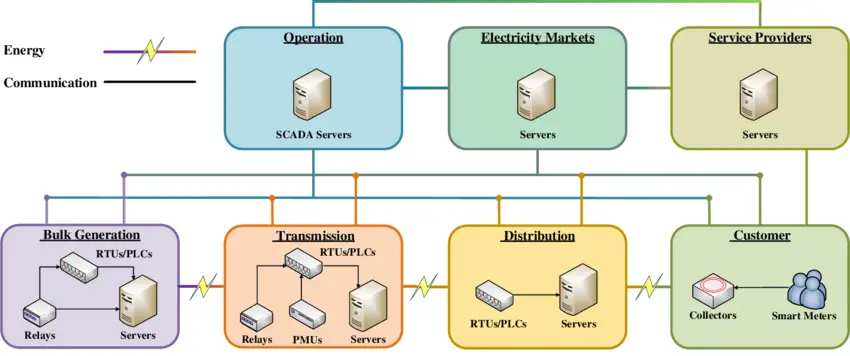
Before developing a robust cyber security strategy, it is crucial to identify and understand the vulnerabilities within the power grid infrastructure. This process typically involves:
- Conducting risk assessments: Perform comprehensive risk assessments to identify potential attack vectors, vulnerabilities in systems and processes, and the likelihood and impact of various cyber threats.
- Evaluating legacy systems: Many power grid components, including industrial control systems (ICS) and supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) systems, may be based on legacy technologies not designed with cyber security in mind. These systems often lack adequate security measures and may require upgrades or replacements.
- Analyzing supply chain risks: The power grid relies on various vendors’ complex supply chains of hardware, software, and services. Assessing the security practices and potential risks associated with each supplier and component is essential.
- Monitoring for emerging threats: Cyber threats are constantly evolving, and it is crucial to stay informed about the latest attack vectors, vulnerabilities, and threat actors targeting the power grid industry.
By conducting thorough vulnerability assessments, we can prioritize our efforts and allocate resources more effectively to address the most critical risks.
Steps to Prepare for a Cyber Attack on the Power Grid
Preparing for a cyber attack on the power grid requires a multi-faceted approach that involves technical, operational, and organizational measures. Here are some critical steps to consider:
- Implement robust cyber security controls: Deploy a comprehensive suite of cyber security controls, including firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS), secure remote access solutions, and advanced threat detection and response capabilities.
- Establish secure network segmentation: Implement network segmentation strategies to isolate critical systems and limit the potential spread of cyber threats within the network.
- Enhance access controls and authentication mechanisms: Implement strong access controls, multi-factor authentication, and privileged access management solutions to protect against unauthorized access and insider threats.
- Develop incident response and recovery plans: Establish well-defined incident response and recovery plans that outline the steps to be taken during a cyber attack, including communication protocols, roles and responsibilities, and recovery procedures.
- Ensure regular software and firmware updates: Maintain a rigorous patch management program to ensure that all software and firmware components are up-to-date with the latest security updates and patches.
- Implement data backup and recovery strategies: Implement robust data backup and recovery strategies to ensure the availability of critical data and systems in the event of a cyber-attack or other disruptive event.
- Foster a culture of cyber security awareness: Promote a robust cyber security culture within the organization by providing regular training and awareness programs for employees, contractors, and stakeholders.
Implementing these steps can significantly enhance our preparedness and resilience against cyber threats targeting the power grid.
Developing a Response Plan for a Cyber Attack on the Power Grid
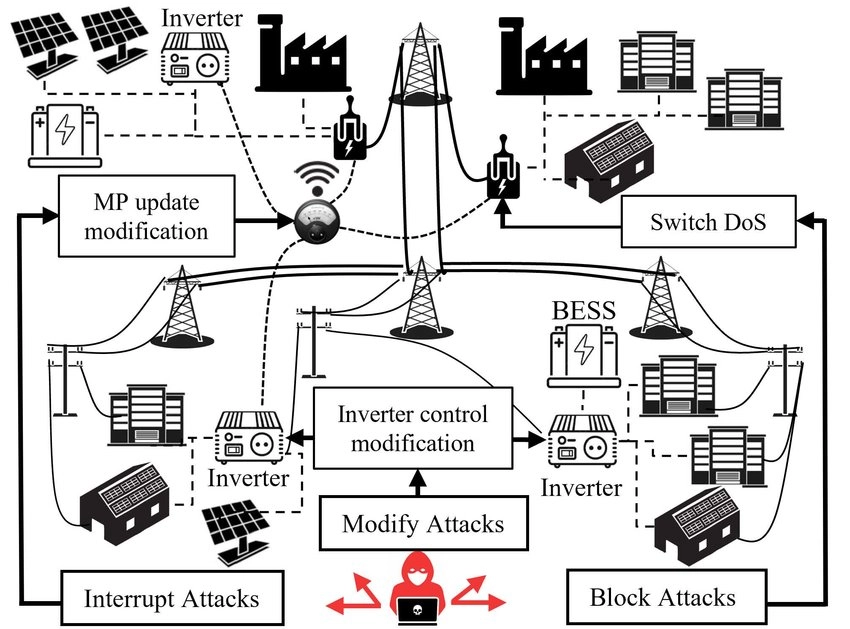
Even with all risk mitigation measures in place, the eventuality of a successful attack could not be entirely eradicated. Hence, a well-defined and rigorously tested response plan has to be in place. Components of an effective response plan:
- Incident response team: Establish a dedicated team with clearly defined roles and responsibilities, including incident commander, technical experts, communication specialists, and legal advisors.
- Incident response procedures: Develop detailed incident response procedures that outline the steps to be taken in various scenarios, such as detecting and containing the attack, investigating the incident, and initiating recovery efforts.
- Communication protocols: Define clear communication protocols for internal and external stakeholders, including regulatory authorities, law enforcement agencies, and the public. Ensure accurate and timely information is disseminated to maintain transparency and manage public perception.
- Coordination with external agencies: Establish partnerships and coordination mechanisms with relevant external agencies, such as law enforcement, cyber security organizations, and industry associations, to facilitate information sharing and collaborative response efforts.
- Tabletop exercises and simulations: Conduct regular tabletop exercises and simulations to test the effectiveness of the response plan, identify gaps or areas for improvement, and ensure that all team members are familiar with their roles and responsibilities.
By developing and regularly testing a comprehensive response plan, we can minimize the impact of a cyber attack and facilitate a more efficient and coordinated recovery effort.
Implementing Preventive Measures to Protect the Power Grid
While the response plans should certainly be efficient and effective, our long-term objective should always be to prevent these attacks from occurring in the first place. Applying such measures at the beginning substantially lessens the chances of successful cyber attacks. It improves the security setup for the power grid. Some of the significant preventive steps include:
- Secure system design and development: Incorporate security principles and best practices throughout the entire system development lifecycle, from design to implementation and maintenance. This includes secure coding practices, architecture design, and rigorous testing and validation processes.
- Continuous monitoring and threat intelligence: Implement constant monitoring and threat intelligence capabilities to promptly detect and respond to potential threats. This may involve deploying security information and event management (SIEM) solutions, threat intelligence platforms, and advanced analytics capabilities.
- Secure remote access and third-party connections: Implement robust security controls for remote access and third-party connections to ensure that these potential attack vectors are adequately protected. This may include multi-factor authentication, secure virtual private networks (VPNs), and strict access control policies.
- Vulnerability management and patch management: Establish a comprehensive vulnerability management program that includes regular vulnerability assessments, risk prioritization, and timely patching of identified vulnerabilities across all systems and components.
- Employee awareness and training: Invest in ongoing employee awareness and training programs to educate personnel on cyber security best practices, identify potential threats, and understand their roles and responsibilities in maintaining a secure environment.
Implementing these preventive measures can significantly reduce the attack surface and minimize the likelihood of successful cyber attacks against the power grid.
Collaborating with Industry Stakeholders for Grid Protection
Protection of the power grid from cyber threats is a joint undertaking that requires a consolidated effort from all stakeholders involved. We will achieve this by building solid partnerships and information-sharing mechanisms and enhancing our collective resilience and response-ability. There are several critical elements of such collaboration:
- Industry associations and working groups: Participate in industry associations and working groups focused on cyber security and grid protection. These forums provide knowledge sharing, best practice exchange, and collective problem-solving opportunities.
- Public-private partnerships: Establish and maintain strong partnerships with government agencies, regulatory bodies, and law enforcement organizations. These partnerships can facilitate information sharing, threat intelligence exchange, and coordinated response efforts.
- Joint exercises and drills: Participate in joint exercises and drills with industry partners, government agencies, and other stakeholders to test and validate response plans, identify areas for improvement, and foster collaboration and coordination.
- Research and development initiatives: Collaborate with academic institutions, research organizations, and technology vendors to drive innovation and develop cutting-edge cybersecurity solutions tailored to the power grid industry’s unique challenges.
- Information sharing and threat intelligence: Participate in industry-wide information sharing and threat intelligence platforms to stay informed about the latest cyber threats, vulnerabilities, and best practices for mitigation and response.
By fostering solid collaborations and leveraging industry stakeholders’ collective expertise and resources, we can enhance our ability to detect, respond to, and recover from cyber attacks targeting the power grid.
Training and Educating Personnel on Cyber Security for the Power Grid
Proper cyber security related to the power grid relies heavily on the knowledge, skills, and awareness of personnel involved in its operation and maintenance. This will entail investments in appropriate training and awareness programs that will allow employees at all levels to be better positioned to identify and mitigate these threats. Following are some of the areas requiring much attention:
- Cyber security awareness training: Provide regular training to all employees, covering topics such as identifying potential threats, recognizing social engineering tactics, and understanding their roles and responsibilities in maintaining a secure environment.
- Technical training for cyber security professionals: Offer specialized training programs for cyber security professionals, covering topics such as network security, incident response, threat hunting, and advanced cyber security tools and techniques.
- Operational training for control room personnel: Provide targeted training for control room personnel, focusing on secure operational practices, incident response procedures, and the importance of maintaining a robust cyber security posture.
- Executive and management training: Educate executives and management on the strategic importance of cyber security, the potential impacts of cyber attacks, and their roles in fostering a robust cyber security culture within the organization.
- Continuous learning and professional development: Encourage and support continuous learning and professional development opportunities for all personnel, ensuring their knowledge and skills remain up-to-date in the rapidly evolving cyber security landscape.
By investing in comprehensive training and education programs, we can cultivate a well-equipped workforce to identify and respond to cyber threats, ultimately enhancing the power grid’s overall security posture.
Related Post: Exploring the 5 Biggest Hacks of All Time
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the most common cyber threats targeting the power grid?
The most common cyber threats against the power grid come from malware attacks, DDoS attacks, APTs, and insider threats. The possible threat actors may be cybercriminals, nation-state actors, or hacktivists.
How can legacy systems in the power grid be secured against cyber threats?
Protection of legacy systems in the power grid can be very complex since most of these were not designed with cybersecurity in mind. Strategies include network segmentation, security appliances or gateways, strict access controls, and monitoring. In some instances, replacing such legacy systems with more secure ones will be required.
What is the role of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) in power grid cyber security?
AI and ML can significantly contribute to cybersecurity in power grids because they allow for advanced threat detection, anomaly detection, and automation of response capabilities. Such technologies analyze vast amounts of data for patterns and anomalies, pointing out cyber threats and making security measures more proactive and efficient.
How can organizations ensure the security of their supply chain in the power grid industry?
Securing this supply chain is paramount in the power grid industry. In general, a vigorous exercise should be exerted to enforce vendor risk management, starting from security assessments and up to the requirements from their audits. This exercise must also include clauses from the service-level agreements that could be reinforced through such contracts. There should be complete visibility of the supply chain, from the hardware and software elements to providing services and personnel.
What are the critical regulatory and compliance requirements for cyber security in the power grid industry?
The power grid industry is subject to various regulatory and compliance requirements about cyber security, including but not limited to those promulgated by the North American Electric Reliability Corporation Critical Infrastructure Protection standards, the National Institute of Standards and Technology Cybersecurity Framework, and others from industry guidelines and best practices.
Conclusion
Protecting the power grid from cyber threats is a critical task that requires a multi-faceted approach and unflinching dedication from all stakeholders. This might be achieved by developing and implementing robust cyber security measures and comprehensive response plans, facilitating collaboration and information sharing, and increasing the investments made in the training and education of personnel. This will significantly enhance the preparedness and resilience to such cyber attacks.