5 Essential Network Security Tips for Cloud Computing
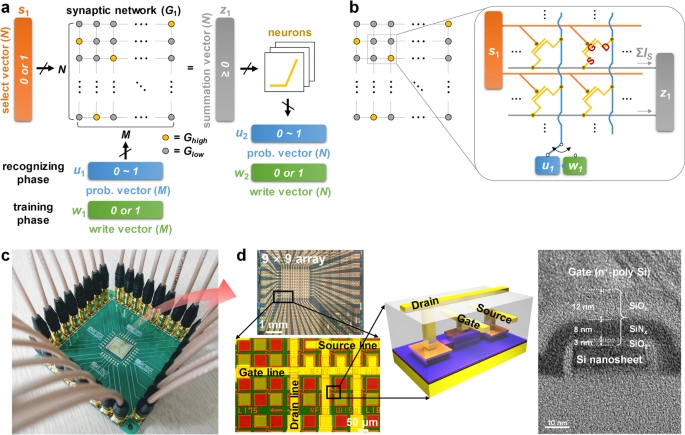
Cloud computing is one of the flexible, scaled, and cost-effective ways a business or individual can store, access, and manage their data and applications over the Internet in this digital age. However, robust network security became imperative with increased reliance on the cloud infrastructure. Cybercriminals never stop seeking new ways to exploit vulnerabilities and gain unauthorized access to sensitive information. This means users must know the risks and take relevant measures to safeguard the cloud environment.
Table of Contents
Understanding the Importance of Network Security in Cloud Computing
Cloud computing has a different set of security concerns that demand special treatment. Unlike the traditional setup of on-premise IT infrastructure, cloud environments are remotely accessible, increasing the attack surface and possibly exposing your data to threats. Another thing is that sharing cloud resources, such as servers and storage, might add to security risks when not managed properly. One has to implement effective network security measures to protect one’s data, maintain compliance, and ensure the general resilience of cloud-based operations.
Tip 1: Implementing Strong Access Controls and User Authentication

Of course, another core pillar in cloud security is good access controls and user authentication. Make sure you have company-wide identity and access management in place, which lets you granularly control who can use your cloud resources and what actions they’re allowed to take on your resources. Implement robust password policies along with multifactor authentication and regularly review and update user permissions to reduce unauthorized access risks to near zero.
Here are some best practices for access controls and user authentication:
- Enforce complex password requirements, including length, character diversity, and regular password changes.
- Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all user accounts, including administrative and privileged access.
- Regularly review and revoke access for terminated or inactive users to prevent unauthorized access.
- Implement role-based access controls (RBAC) to ensure users have the minimum permissions to perform their tasks.
- Regularly audit and monitor user activities to detect and respond to suspicious behavior.
Tip 2: Regularly Update and Patch Your Cloud Infrastructure
Keeping your cloud infrastructure updated with the latest security patches and updates is critical for a secure environment. Cloud service providers continually release security patches and updates that counter known vulnerabilities and nascent threats. Kindly update these releases without any delay to prevent your cloud environment from being exploited by malicious actors.
Here’s how you can ensure your cloud infrastructure is correctly updated and patched:
- Establish a regular patching and update schedule for your cloud resources, including virtual machines, databases, and third-party software or services.
- Enable automated patching and updates whenever possible to ensure your environment is always up-to-date.
- Monitor and review release notes from your cloud service provider to stay informed about the latest security updates and their potential impact on your environment.
- Test updates and patches in a non-production environment before deploying them to your live systems to ensure compatibility and avoid disruptions.
- Maintain a comprehensive inventory of your cloud resources and patch levels to ensure complete visibility and control.
Tip 3: Encrypt Your Data to Protect It from Unauthorized Access
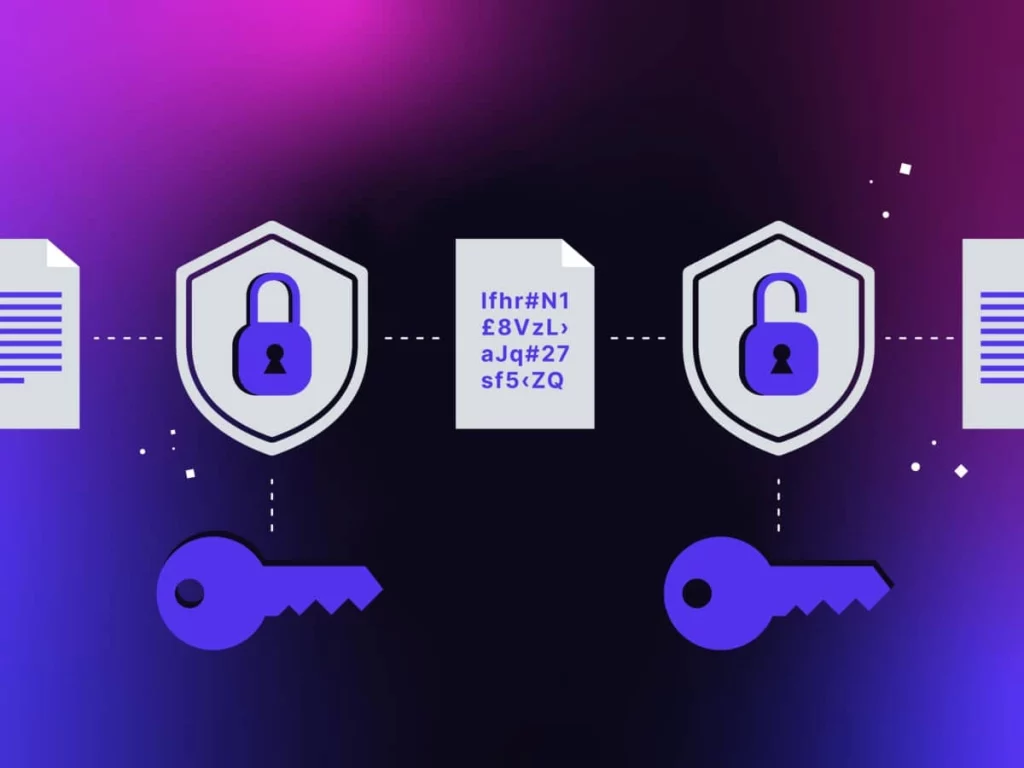
Data encryption has become essential for network safety in the cloud. Data that is encrypted is rendered unreadable to any other entity if it is hijacked or stolen. All CSPs usually provide a facility for data encryption. Still, awareness of these measures and how to correctly apply them is required.
Here are some best practices for data encryption in the cloud:
- Encrypt data at rest, such as in cloud storage or databases, using robust encryption algorithms like AES-256.
- Encrypt data in transit using secure protocols like HTTPS, SSL/TLS, or VPNs to protect it as it moves between your local environment and the cloud.
- Manage your encryption keys, known as customer-managed keys, to maintain control over your data’s encryption and reduce the risk of unauthorized access.
- Implement data loss prevention (DLP) strategies to monitor and protect sensitive data from unauthorized access or exfiltration.
- Review and update your encryption policies and practices regularly to ensure they keep pace with evolving security standards and threats.
Tip 4: Backup Your Data Regularly to Ensure Business Continuity

A dependable backup strategy is a must to ensure business continuity and resilience after security breaches, data loss, or system failure. Cloud-based solutions are at hand to protect critical data more efficiently and more scalable. However, this must be implemented correctly, and backing up and restoring procedures must be done regularly.
Here are some critical considerations for effective data backup in the cloud:
- Implement a comprehensive backup strategy that includes both on-premises and cloud-based backups, which can restore data to different locations or environments.
- Ensure your backup data is encrypted and stored in a secure, geographically diverse location to protect against regional disasters or localized threats.
- Regularly test your backup and restore processes to ensure your data can be recovered during an incident.
- Establish clear backup and retention policies that align with your business requirements and regulatory compliance needs.
- Monitor your backup processes and set up alerts to notify you of any failures or anomalies, allowing you to address issues promptly.
Tip 5: Monitor and Analyze Your Network Traffic for Potential Threats

This demands constant monitoring and analysis of cloud network traffic in these contexts to detect and respond to any security threats. The following ensures that by monitoring your network activities closely, you can detect anomalies, identify suspicious behavior, and verify indications of compromise to take adequate measures against such risks.
Here are some best practices for network traffic monitoring and analysis in the cloud:
- Implement a cloud-based network monitoring and security information and event management (SIEM) solution to centralize the collection and analysis of your network data.
- Configure your monitoring tools to alert you to suspicious activity, such as unusual login attempts, data exfiltration, or unauthorized access to sensitive resources.
- Review and analyze your network logs and security event data regularly to identify potential threats and trends and to fine-tune your security controls.
- Integrate your network monitoring with other security tools, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and cloud security posture management (CSPM) solutions, to enhance your overall visibility and response capabilities.
- Establish clear incident response and threat-hunting processes to ensure your team can quickly investigate and mitigate any identified security incidents.
Tools and Technologies for Enhancing Network Security in the Cloud
A wide range of tools and technologies are available to help you enhance your network security in the cloud. Some of the critical solutions to consider include:
- Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB): CASB solutions provide visibility and control over cloud applications and data, helping you to identify and mitigate security risks.
- Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM): CSPM tools monitor your cloud infrastructure for misconfigurations, vulnerabilities, and compliance issues and provide recommendations for remediation.
- Cloud Workload Protection Platform (CWPP): CWPP solutions protect your cloud-based workloads, such as virtual machines and containers, from security threats and vulnerabilities.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): SIEM platforms collect, analyze, and correlate security-related data across your cloud environment, enabling you to detect and respond to security incidents.
- Virtual Private Network (VPN): VPNs establish secure, encrypted connections between your local environment and the cloud, protecting your data in transit.
Read Also: Effective Content Marketing: Strategies for Success
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- How do I ensure that my cloud service provider maintains proper security controls?
- Carefully review your cloud service provider’s security and compliance certifications, such as SOC 2, ISO 27001, and FedRAMP.
- Review your cloud service provider’s security policies, incident response plans, and third-party audit reports regularly.
- Establish security and compliance requirements in your service-level agreements (SLAs) with your cloud service provider.
- What are the most common cloud security threats I should be aware of?
- Unauthorized access to cloud resources, such as through credential theft or misconfigured access controls.
- Data breaches and data loss due to inadequate data protection measures.
- Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks that can disrupt your cloud-based services.
- Malware and ransomware can compromise your cloud infrastructure and data.
- Insider threats, where malicious or negligent insiders abuse their access privileges.
- How can I ensure compliance with regulatory requirements in the cloud?
- Understand the specific compliance requirements that apply to your organization and cloud-based operations.
- Implement controls and processes to meet these compliance requirements, such as data encryption, access controls, and logging and monitoring.
- Regularly audit your cloud environment and document your compliance efforts to demonstrate adherence to regulatory standards.
- Engage with your cloud service provider to ensure their security and compliance measures align with your needs.
Please do not hesitate to schedule your consultation with one of our security experts today. They will help you strategize and put in place tools and technologies to provide top-notch security for your cloud environment.
Conclusion
With the ever-increasing importance of cloud computing in changing how we work and do business, network security has never been needed more than now. Suppose you have robust access controls, regular patching and updating, data encryption, reliable backup arrangements, and continuous monitoring. In that case, you will have enough measures to protect your precious data from a wide array of threats against your cloud security.