What Types of Technology Have Helped the Gig Economy Grow
The gig economy’s growth is characterized by short-term contracts, freelance work, if not permanent, and full-time jobs in the labor market. This model allows people to be independent contractors, moving from project to project and frequently using their equipment and competencies to offer services to clients or customers. The gig economy has been dramatically empowered over the last few years, giving people flexibility and autonomy to select work arrangements and work-life balance.
Table of Contents
The Impact of Technology on the Gig Economy
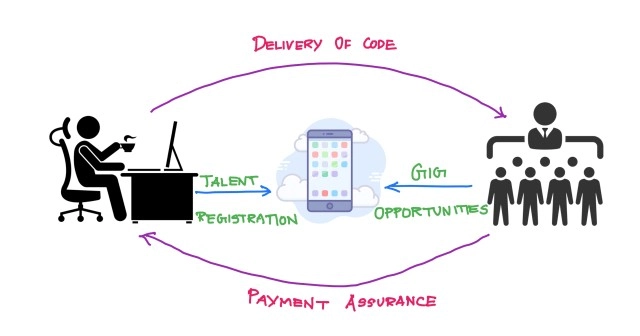
This remarkable growth can be attributed to the transformative effect of technology on this gig economy to a great extent. Innovative technological solutions have changed how people find, perform, and get paid for their work. Technology has become the backbone of the gig economy, from online platforms to mobile apps, communication tools, and state-of-the-art payment systems, enabling more efficiency, accessibility, and connectivity.
Types of Technology that Have Helped the Gig Economy Grow
Mobile Apps and the Gig Economy

Mobile applications have formed a significant part of the rise of the gig economy. Indeed, platforms like Uber, Lyft, Upwork, and even Fiverr have effectively employed mobile technology to match buyers and sellers in real time, thus allowing for on-demand and flexible work arrangements. These applications have facilitated much easier access for many people to gig opportunities—from ride-sharing and delivery services to freelance and professional service work.
Online Platforms and the Gig Economy
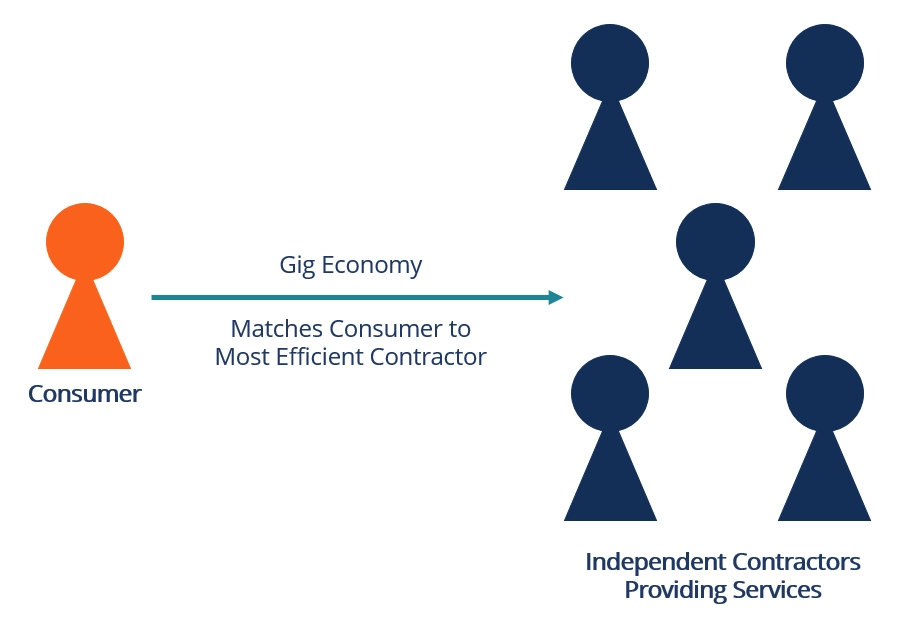
The rise of online platforms does shift the dynamics for gig economy workers. Sites and online marketplaces such as Freelancer, Upwork, and Fiverr have literally put a hub at their fingertips—to open freelancers, independent contractors, and gig workers to clients seeking project-based help. Typically, these platforms provide features such as job posting, proposal submission, secure payment processing, and streamlining and facilitating all processes concerning finding and finishing gig work.
Communication Tools and the Gig Economy

Communication in the gig economy is at the core of how things get done, characterized by remote work and distributed teams. Collaboration and communication tools, aided by Slack, Zoom, and Microsoft Teams, have made remote work for gig workers effortless. From coordinating with clients to working on projects to remaining plugged into one’s network, no matter their geolocation, these tools facilitated real-time communication, file sharing, and project management, all critical for gig workers in giving top-notch work while keeping a solid relationship with clients.
Payment Systems and the Gig Economy

The gig economy also thrives on robust and safe payment systems. Online payment portals like PayPal, Stripe, and Venmo have revolutionized how individuals in this type of work are paid. These tools provide fast, effective, and secure processing of payments that enable gig workers to be compensated quickly for services offered. Integrating such payment systems into the gig economy has further streamlined the financial aspects of gig work. It makes it easier for workers and clients when dealing with transactions.
Marketplace Platforms for Services

Marketplace platforms like Uber, Airbnb, and Upwork have revolutionized how gig work is found and fulfilled. These platforms connect gig workers directly with customers, facilitating a smooth transaction process and providing a reliable source of income for millions worldwide.
Examples: Uber, Airbnb
Uber and Airbnb are excellent examples of how technology provides new business models in the gig economy. By giving people new ways to earn, they disrupt the service industry, changing it fundamentally with technology that bridges gaps between supply and demand.
Technology’s Role in Enabling Remote Work
One significant way technology has impacted the gig economy is by facilitating remote work. The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated this shift to remote work, with the gig economy at the front. Advances in video conferencing, cloud-based collaboration tools, and project management software have made remote work by gig workers possible worldwide. This has expanded the pool of available talent and opportunities for workers and clients.
The Future of Technology in the Gig Economy
Technology will become intrinsic in the gig economy in times to come. Newer technologies such as Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, and Blockchain will further revolutionize the gig economy. For example, AI-driven algorithms can match gig workers and appropriate job opportunities. At the same time, blockchain technology could completely turn upside-down transaction and payment arrangements, bringing in a new level of transparency and security. This space can bundle the IoT, smart devices, and other new technologies, making gig work possible, from remote home services to on-demand delivery.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the gig economy, and how does it differ from traditional employment?
The gig economy is characterized by a job market dominated by short-term, freelance-type contracts instead of permanent and full-time employment. It is work contracted on a project-by-project basis, usually an arrangement wherein one is self-equipped with the necessary materials or skills to provide services to clients or customers. This model offers greater flexibility and autonomy compared to traditional employment.
How has technology impacted the growth of the gig economy?
Technology has been the principal driving force behind the gig economy. Successive innovations changed how individuals found, did, and got paid for work, from mobile apps and online platforms to communication tools and innovative payment systems. The technological fixes made access to various opportunities easier for the gig workers and helped them collaborate with the clients and manage their finances.
What are some examples of technologies that have enabled the gig economy?
Some key technologies that have fueled the growth of the gig economy include:
Mobile apps (e.g., Uber, Lyft, Upwork, Fiverr)
Online platforms (e.g., Freelancer, Upwork, Fiverr)
Communication tools (e.g., Slack, Zoom, Microsoft Teams)
Payment systems (e.g., PayPal, Stripe, Venmo)
How has remote work impacted the gig economy?
The gig economy has been driven in large part by remote work. Improvements to video conferencing, cloud collaboration tools, and project management software help gig workers execute their duties efficiently worldwide. This has led to an ever-expanding pool of available talent and opportunities between workers and clients, further fueling the gig economy’s growth.
What is the future of technology in the gig economy?
The gig economy will see further disruption in technology in the future. Artificial intelligence, machine learning, blockchain, and the Internet of Things—all new technologies—are likely to change the modus operandi of the gig economy. These could be applied in more efficient matching, enhancing the security of transactions, and even creating new forms of gig work that further cement technology’s place as the spine of the gig economy.
Read Also: Power of a Generalist AI Agent in 3D Virtual Environments
Conclusion
The gig economy has seen a sea change, dictated to a considerable extent by the pace of technology growth. From mobile apps and online sites to communication tools and secure payment systems, technology has become the gig economy’s bedrock. As the world continues to evolve further, the role of technology in this gig economy will only increase in importance—changing how people find, perform, and get paid for their work. In other words, adopting these kinds of technological innovations is likely to lend further impetus to the growth of the gig economy and continue to offer more flexibility, autonomy, and opportunity to people seeking alternative employment models.
Want more on how technology is putting juice behind the gig economy’s future? Subscribe to our newsletter, where we’ll keep you up-to-date with the latest trends, insights, and opportunities in this dynamic and ever-evolving space.