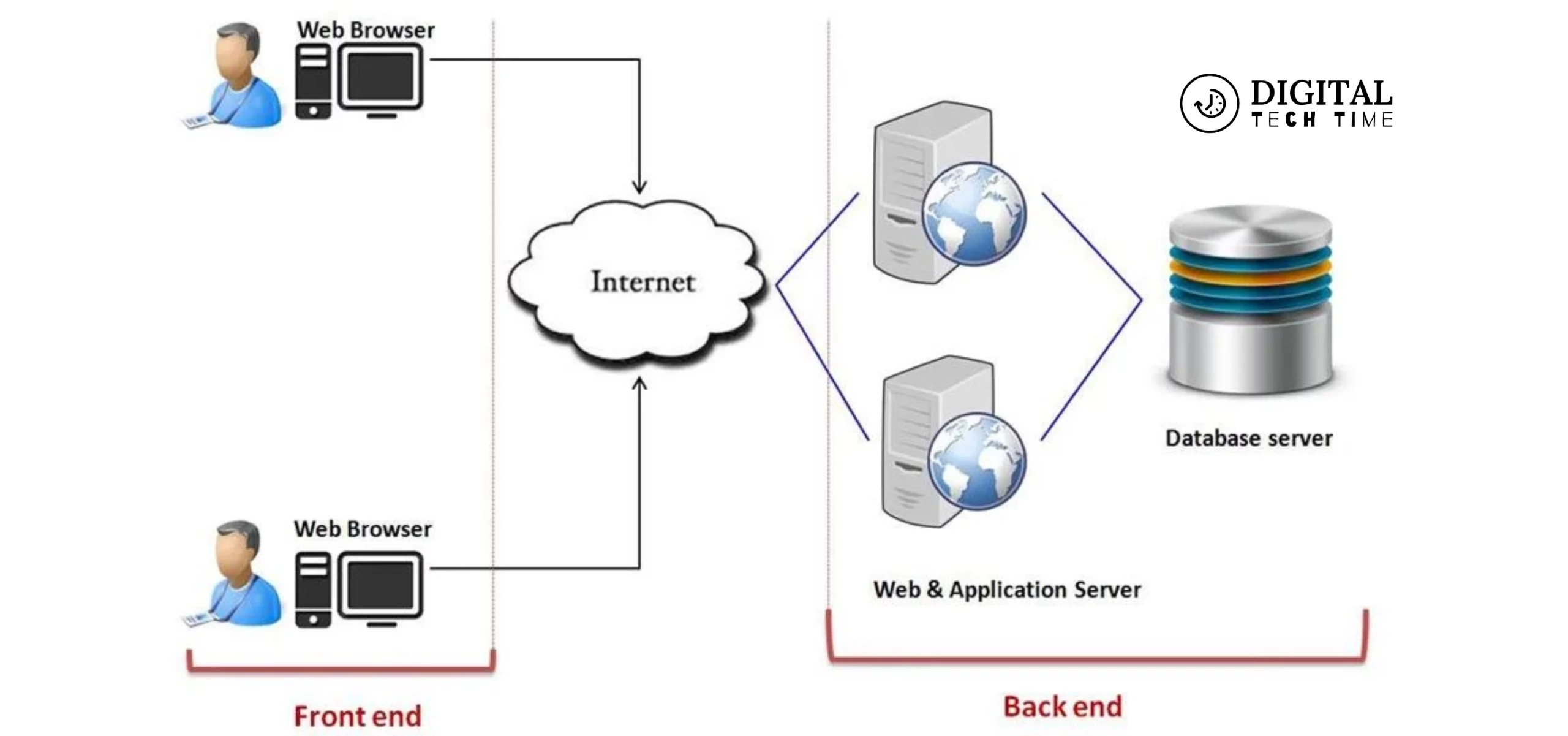
3 Basic Components of Cloud Computing
In today’s digital landscape, cloud computing has emerged as a transformative force, reshaping how businesses operate and individuals access and store data. As we delve deeper into this realm, it becomes crucial to understand the fundamental building blocks that form the foundation of this revolutionary technology. Cloud computing, in essence, is a paradigm shift that allows users to access and utilize computing resources on demand without the need for extensive hardware or infrastructure investments.
At its core, cloud computing revolves around three essential components: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). These components form the backbone of the cloud computing ecosystem, enabling businesses and individuals to leverage the power of the cloud in various ways. This article will explore these three essential components, their unique characteristics, and how they contribute to the overall cloud computing experience.
Table of Contents
What are the Essential Components of Cloud Computing?
The three essential components of cloud computing are:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
- Platform as a Service (PaaS)
- Software as a Service (SaaS)
Each component serves a distinct purpose and caters to different needs, offering businesses and individuals various options to effectively leverage the cloud’s capabilities.
Component 1: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
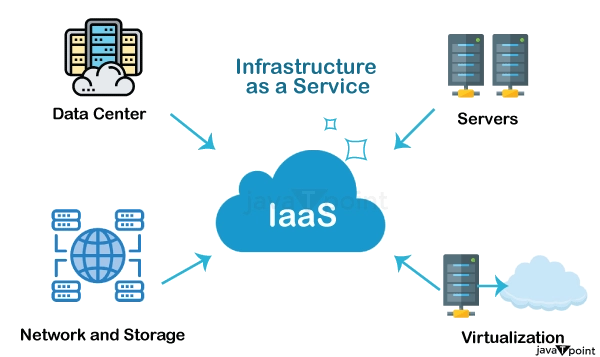
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) is the foundational layer of cloud computing. It provides users access to virtualized computing resources, such as servers, storage, networking, and other essential infrastructure components, on a pay-as-you-go basis. With IaaS, organizations can quickly provision and scale their computing resources without investing in physical hardware or managing complex data centers.
Key features of IaaS include:
- Virtualized Computing Resources: IaaS offers virtualized computing resources, including virtual machines (VMs), storage, and networking, enabling users to create and manage their virtual infrastructure.
- Scalability: IaaS allows for dynamic scaling of resources based on demand, ensuring that organizations have access to the computing power they need when needed.
- Cost-Efficiency: IaaS provides a cost-effective solution for businesses of all sizes by eliminating the need for upfront capital investments and ongoing maintenance costs.
- Flexibility: IaaS offers flexibility in terms of resource allocation, allowing users to provision and de-provision resources as needed, ensuring optimal resource utilization.
Examples of popular IaaS providers include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2), Microsoft Azure Virtual Machines, and Google Cloud Platform Compute Engine.
Component 2: Platform as a Service (PaaS)
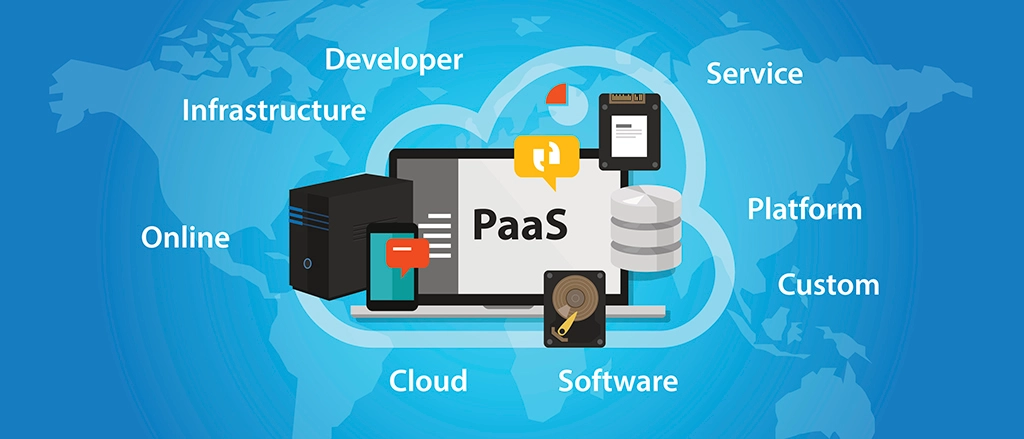
Platform as a Service (PaaS) is the next layer in the cloud computing stack. It provides a complete development and deployment environment, including hardware, operating systems, databases, and other tools for building and running applications. With PaaS, developers can focus on writing code and deploying applications without worrying about the underlying infrastructure.
Critical features of PaaS include:
- Rapid Application Development: PaaS offers a streamlined development environment, enabling developers to build, test, and deploy applications quickly and efficiently.
- Integrated Tools and Services: PaaS providers typically offer integrated tools and services, such as code editors, version control systems, and deployment tools, facilitating a seamless development experience.
- Scalability and Elasticity: PaaS platforms are designed to scale up or down automatically based on application demand, ensuring optimal performance and resource utilization.
- Multi-Tenancy: PaaS platforms support multi-tenancy, allowing multiple applications to run on shared resources while maintaining data isolation and security.
Popular PaaS providers include Google App Engine, Microsoft Azure App Service, and AWS Elastic Beanstalk.
Component 3: Software as a Service (SaaS)
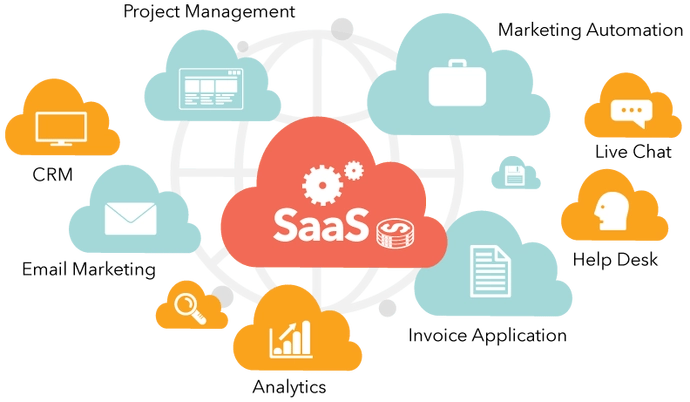
Software as a Service (SaaS) is the top layer of the cloud computing stack, offering ready-to-use software applications delivered over the internet. With SaaS, users can access and use software applications without needing installation, maintenance, or hardware investments. SaaS applications are typically accessible through web browsers or dedicated client applications, providing a convenient and scalable solution for businesses and individuals.
Critical features of SaaS include:
- On-Demand Access: SaaS applications are accessible from any device with an internet connection, allowing users to access and use the software on demand.
- Automatic Updates: SaaS providers handle software updates and upgrades, ensuring users can always access the latest features and security patches.
- Subscription-Based Pricing: SaaS applications are typically offered on a subscription-based pricing model, which allows users to pay for their use, reduces upfront costs, and provides predictability.
- Collaboration and Accessibility: SaaS applications often provide collaboration tools and centralized data storage, enabling teams to work together seamlessly, regardless of location.
Examples of popular SaaS applications include Google Workspace (formerly G Suite), Microsoft Office 365, Salesforce, and Dropbox.
Benefits of Cloud Computing
Embracing cloud computing offers numerous benefits for businesses and individuals alike. Here are some key advantages:
- Cost Savings: By leveraging cloud computing services, organizations can avoid the upfront costs of purchasing and maintaining hardware and software, leading to significant cost savings.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Cloud computing allows for easy scaling of resources up or down based on demand, ensuring optimal resource utilization and enabling organizations to adapt quickly to changing business needs.
- Accessibility and Mobility: With cloud computing, users can access data and applications from anywhere with an internet connection, promoting mobility and enabling remote work scenarios.
- Disaster Recovery and Data Security: Cloud service providers typically offer robust disaster recovery and data backup solutions, ensuring business continuity and data protection in unforeseen circumstances.
- Reduced Maintenance and Overhead: By outsourcing infrastructure and software management to cloud providers, organizations can ease the burden of maintaining and updating systems, freeing up resources for core business activities.
Real-World Examples and Use Cases
Numerous organizations across various industries have embraced IaaS to streamline their IT operations and accelerate innovation. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) providers such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) are used by startups and established businesses to run apps, host websites, and safely store data in the cloud.
Examples of Cloud Computing Services
To better understand the practical applications of cloud computing, let’s explore some real-world examples of popular cloud computing services:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS): AWS offers a comprehensive suite of cloud computing services, including EC2 (IaaS), Lambda (serverless computing), S3 (object storage), and many more.
- Microsoft Azure: Azure provides a wide range of cloud services, such as Virtual Machines (IaaS), App Services (PaaS), Azure SQL Database, and Azure Cognitive Services for AI and machine learning.
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP): GCP offers services like Compute Engine (IaaS), App Engine (PaaS), Cloud Storage, and advanced data analytics and machine learning tools.
- Salesforce: Salesforce is a leading SaaS platform for customer relationship management (CRM), offering a suite of cloud-based applications for sales, marketing, and customer service.
- Dropbox: Dropbox is a popular cloud storage and file-sharing service that allows users to store, access, and collaborate on files from anywhere.
These examples illustrate the diverse cloud computing services available, catering to various business needs and industries.
Choosing the Right Cloud Computing Components for your Business
When selecting the appropriate cloud computing components for your business, assessing your specific requirements and goals is essential. Here are some key factors to consider:
Business Needs: Evaluate your business objectives, workloads, and the applications or services you require. This will help determine whether you need IaaS for infrastructure provisioning, PaaS for application development, or SaaS for ready-to-use software solutions.
Scalability and Performance: Consider your current and future scalability needs and the performance requirements of your applications. IaaS and PaaS solutions may suit workloads with variable resource demands or high-performance computing needs.
Cost and Budget: Analyze the costs associated with each cloud computing component, considering factors such as usage patterns, data transfer costs, and long-term cost projections. SaaS solutions may be more cost-effective for smaller businesses with predictable usage patterns.
Security and Compliance: Assess your industry’s security and compliance requirements and the security measures offered by cloud service providers. Some industries, such as healthcare or finance, may have stricter regulations that must be considered.
Integration and Compatibility: Evaluate the cloud services’ integration capabilities with your existing systems and applications. Ensure that the chosen components seamlessly integrate with your existing infrastructure and workflows.
Vendor Reputation and Support: Consider the cloud service provider’s reputation, reliability, and support offerings. Reputable vendors with robust support and service-level agreements (SLAs) can provide peace of mind and ensure business continuity.
Read Also: Cloud Services: A Comprehensive Guide
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the difference between IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS?
IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service) provides virtualized computing resources, such as servers, storage, and networking, allowing users to build and manage their virtual infrastructure.
PaaS (Platform as a Service) offers a complete development and deployment environment, including hardware, operating systems, databases, and tools for building and running applications.
SaaS (Software as a Service) delivers ready-to-use software applications over the internet, accessible through web browsers or dedicated client applications.
Can I use multiple cloud computing components together?
It is possible to combine different cloud computing components to create a comprehensive solution tailored to your specific needs. For example, you can use IaaS for infrastructure provisioning, PaaS for application development, and SaaS for specific software requirements.
Is cloud computing secure?
Cloud service providers implement robust security measures, such as data encryption, access controls, and regular security updates, to protect user data and applications. However, choosing reputable providers and following best practices for data security and compliance is essential.
How does cloud computing pricing work?
Cloud computing services typically follow a pay-as-you-go or subscription-based pricing model. Users are charged based on their actual usage of resources, such as computing power, storage, and bandwidth consumption. This model allows for cost predictability and flexibility.
Can I migrate my existing applications to the cloud?
Many cloud service providers offer tools and services to facilitate migrating existing applications to the cloud. This process, known as cloud migration, can help organizations leverage the benefits of cloud computing while minimizing disruptions to their existing systems.
Conclusion
Cloud computing has revolutionized how we access and utilize computing resources, offering unparalleled flexibility, scalability, and cost-efficiency. The three essential components of cloud computing—infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS)—form the foundation of this transformative technology.