How Can Edge Computing Be Used to Improve Sustainability?
In our rapidly evolving digital landscape, pursuing technological advancement often contradicts the imperative need for environmental sustainability. However, the emergence of edge computing presents a promising solution that harmonizes these seemingly disparate goals. By bringing computational power closer to the source of data generation, edge computing enhances efficiency and reduces the environmental footprint associated with traditional cloud computing models.
Table of Contents
Understanding the concept of edge computing
What is Edge Computing?
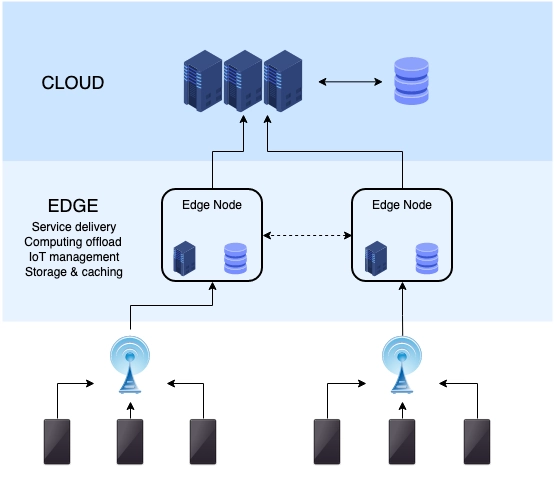
Edge computing is a distributed computing paradigm that brings data processing and storage capabilities closer to the devices where data is generated or consumed. Instead of transmitting vast amounts of raw data to centralized cloud servers for processing, edge computing enables computation and analysis at or near the source, minimizing the need for long-distance data transfer.
By processing data locally, edge computing reduces the strain on network bandwidth and mitigates latency issues. This enables real-time decision-making and enhances the overall performance of applications and services. This decentralized approach is particularly beneficial for scenarios that require rapid response times, such as autonomous vehicles, industrial automation, and remote monitoring systems.
Edge vs. Cloud Computing
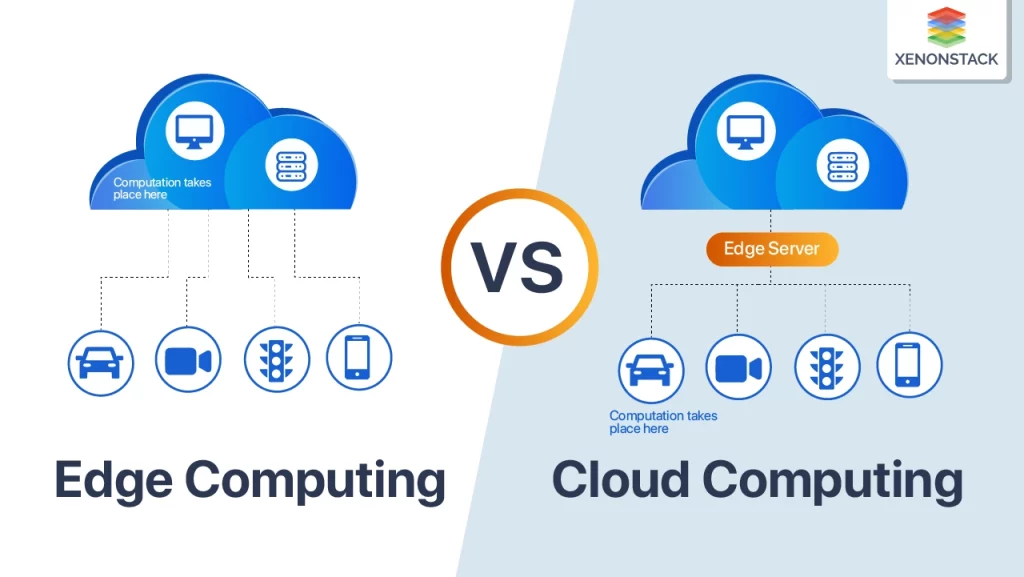
While cloud computing relies on centralized data centers to process and store data, edge computing distributes computational resources across a network of localized devices or edge nodes. This decentralized architecture offers several advantages over traditional cloud-based models:
- Reduced Latency: By processing data closer to its source, edge computing minimizes the time required for data to travel to and from the cloud, enabling real-time decision-making and responsiveness.
- Bandwidth Optimization: Only processed or filtered data must be transmitted to the cloud, reducing the bandwidth requirements and associated costs.
- Increased Reliability: Edge computing systems can continue operating even when cloud connectivity is disrupted, ensuring uninterrupted service delivery.
- Enhanced Privacy and Security: Data processing at the edge minimizes the need to transmit sensitive information over the internet, reducing the risk of data breaches and privacy violations.
Technologies Enabling Edge Computing
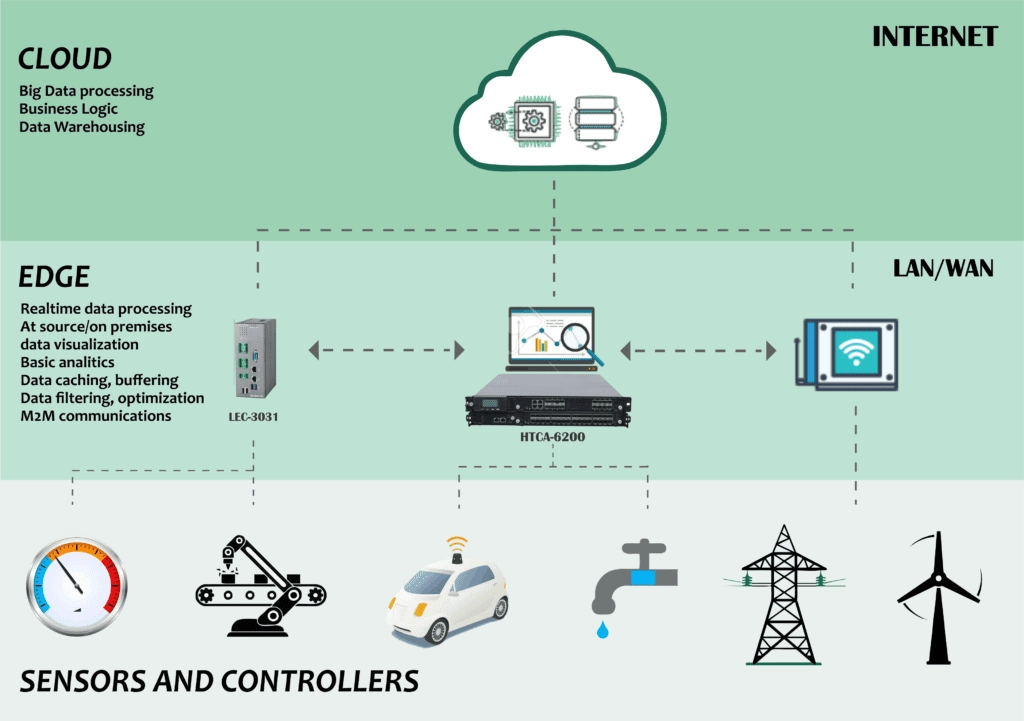
The rise of edge computing has been facilitated by advancements in various technologies, including:
- Internet of Things (IoT): The proliferation of connected devices and sensors has generated massive amounts of data that require processing at the edge.
- 5G and Low-Power Wide Area Networks (LPWANs): High-speed and low-latency wireless connectivity enables efficient data transmission and processing at the edge.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): Sophisticated algorithms and models can be deployed at the edge to analyze and extract insights from data in real time.
- Edge Computing Hardware: Specialized hardware, such as edge gateways, single-board computers, and intelligent sensors, are designed to perform computations at the edge.
Digital Demand vs. Sustainability
As our reliance on digital technologies grows, so does the energy consumption and environmental impact associated with data centers and cloud computing infrastructure. The insatiable demand for data processing and storage has led to a significant carbon footprint, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions and exacerbating the effects of climate change.
According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), data centers and data transmission networks accounted for approximately 1% of global electricity consumption in 2020, and this figure is projected to rise substantially in the coming years. Addressing this challenge is crucial for achieving a sustainable digital future.
Case Studies: Success Stories
Edge computing has already demonstrated its potential to drive sustainability initiatives across various industries. Here are a few success stories that highlight the transformative power of this technology:
- Intelligent Cities: Edge computing is pivotal in developing smart cities by enabling real-time monitoring and optimization of urban infrastructure, such as traffic management, waste collection, and energy distribution. For example, Barcelona has implemented an edge computing solution to analyze data from IoT sensors, optimize street lighting, and reduce energy consumption by up to 25%.
- Precision Agriculture: By deploying edge computing devices in agricultural settings, farmers can monitor soil conditions, weather patterns, and crop health in real time, enabling precise and targeted interventions. This approach minimizes using resources like water and fertilizers, reduces environmental impact, and promotes sustainable farming practices.
- Industrial Automation: Edge computing enables predictive maintenance and real-time optimization of industrial processes, leading to increased efficiency, reduced downtime, and lower energy consumption. For instance, a manufacturing facility in Germany has implemented an edge computing system to monitor and optimize its production lines, resulting in a 20% reduction in energy usage.
Privacy and Security Concerns

While edge computing offers numerous benefits, addressing the associated privacy and security concerns is essential. Distributing data processing across multiple edge nodes increases the attack surface for potential cyber threats. Ensuring robust data encryption, access control mechanisms, and secure communication protocols is crucial to mitigating these risks.
Additionally, the decentralized nature of edge computing raises questions about data ownership and privacy. Clear policies and regulations must be established to protect individual privacy rights and ensure compliance with data protection laws.
How can edge computing be used to improve sustainability?
How Can Edge Computing Be Used to Improve Sustainability?
Edge computing presents a transformative opportunity to enhance sustainability across various domains. By processing data at the source and minimizing the need for long-distance data transmission, edge computing reduces the energy consumption associated with traditional cloud computing models. Here are some key ways in which edge computing can be leveraged to improve sustainability:
- Optimizing Energy Consumption: Edge computing enables real-time energy usage monitoring and optimization in buildings, factories, and infrastructure. By analyzing data from sensors and IoT devices at the edge, intelligent systems can automatically adjust lighting, heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems, leading to significant energy savings.
- Enabling Smart Grids: Integrating edge computing with smart grid technology can revolutionize how we manage and distribute electricity. Edge devices can monitor and control energy generation, storage, and consumption, facilitating the integration of renewable energy sources and improving grid efficiency.
- Reducing Data Center Emissions: By offloading computational tasks to edge devices, the demand for energy-intensive data centers can be reduced, leading to lower greenhouse gas emissions and a smaller carbon footprint.
- Facilitating Sustainable Transportation: Edge computing is crucial in developing autonomous and connected vehicles, enabling real-time data processing for navigation, traffic optimization, and predictive maintenance. This improves safety and efficiency and contributes to reducing emissions and promoting sustainable transportation solutions.
- Enabling Precision Agriculture: Edge computing empowers precision agriculture practices by analyzing data from sensors, drones, and other IoT devices deployed in agricultural settings. This allows for targeted and efficient use of resources like water, fertilizers, and pesticides, minimizing waste and environmental impact.
Real-world examples of edge computing for sustainability
To further illustrate the potential of edge computing in driving sustainability initiatives, let’s explore some real-world examples:
- Smart Building Management: Companies like Siemens and Honeywell have developed edge computing solutions for building automation and energy management. These systems analyze data from sensors and IoT devices to optimize heating, cooling, lighting, and ventilation, resulting in significant energy savings and reduced carbon emissions.
- Precision Agriculture: Startups like Prospera and FarmWise have leveraged edge computing and AI to develop intelligent systems for precision farming. These solutions monitor crop health, soil conditions, and weather patterns, enabling targeted interventions and minimizing resource waste.
- Smart Grid Integration: Companies like Itron and Landis+Gyr have implemented edge computing solutions to enable smart grid functionality. These systems analyze intelligent meters and grid sensor data to optimize energy distribution, integrate renewable sources, and provide real-time insights to utilities and consumers.
- Sustainable Transportation: Automotive companies like Tesla and Waymo are at the forefront of integrating edge computing into their autonomous and connected vehicle technologies. These systems process data from sensors and cameras in real time, enabling efficient navigation, predictive maintenance, and reduced emissions.
Read Also: What Is a Barrier to Entry Preventing Quantum Computing?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the difference between edge computing and cloud computing?
Edge computing brings data processing and storage capabilities closer to the source of data generation, while cloud computing relies on centralized data centers. Edge computing reduces latency, optimizes bandwidth, and enhances privacy and security.
How does edge computing contribute to sustainability?
Edge computing reduces energy consumption and the associated carbon footprint by processing data locally and minimizing long-distance data transmission. It also enables real-time optimization of energy usage, facilitates intelligent grids, and supports sustainable practices in various industries.
What are the leading technologies enabling edge computing?
Key technologies enabling edge computing include the Internet of Things (IoT), 5G and Low-Power Wide Area Networks (LPWANs), Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML), and specialized edge computing hardware.
Are there any privacy and security concerns associated with edge computing?
The distributed nature of edge computing increases the potential attack surface for cyber threats. Robust data encryption, access control mechanisms, and secure communication protocols are essential to mitigate these risks. Clear policies and regulations must also be established to protect individual privacy rights.
Can edge computing be integrated with existing cloud computing infrastructure?
Yes, edge computing and cloud computing can coexist and complement each other. Edge computing can offload computational tasks from the cloud, while the cloud can provide centralized storage, management, and backup capabilities for edge devices.
Conclusion
As we navigate the challenges of our digital age, edge computing emerges as a powerful ally in pursuing a sustainable future. By bringing computational power closer to the source of data generation, this innovative technology offers a unique opportunity to harmonize technological advancement with environmental stewardship.
Through real-time optimization of energy usage, integration with smart grids, and enabling sustainable practices across various industries, edge computing has the potential to significantly reduce our carbon footprint and mitigate the environmental impact of our digital endeavors.