Solving the Connection Limit Error in Windows: A Step-by-Step Guide
Understanding and resolving this issue is paramount. When connection limits are reached, it can halt productivity, restrict access to critical applications, and delay the timely completion of tasks. In environments like small businesses, educational institutions, or even large enterprises using remote access for their operations, these disruptions can lead to significant downtime, affecting everything from day-to-day operations to critical communications.
Table of Contents
Step-by-Step Solutions
Step 1: Disconnect from the Network
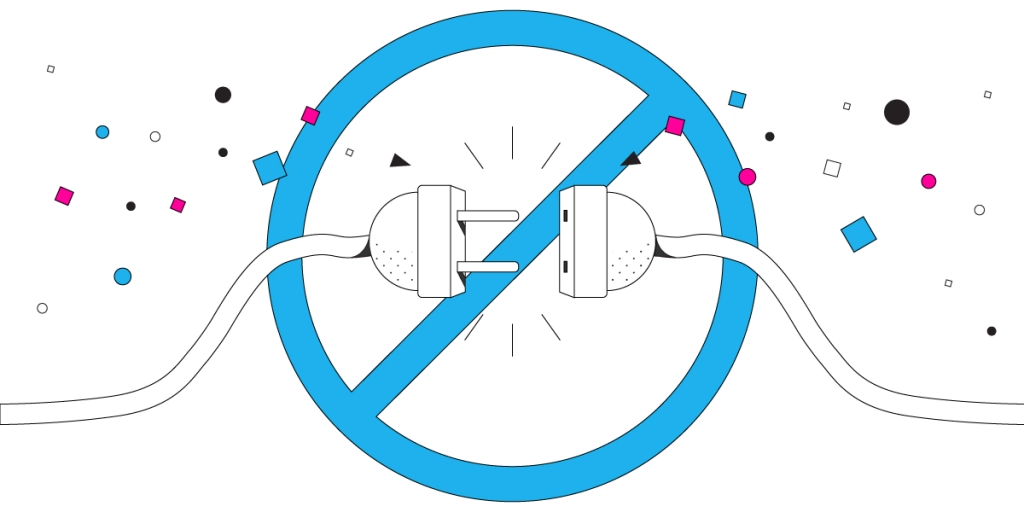
- Action: Unplug your network cable or turn off your WiFi.
- Purpose: This step ensures that all current network sessions are completely terminated. It prevents any existing connections that may be unrecognized or improperly closed from counting against your connection limit.
Step 2: Reboot Your Computer
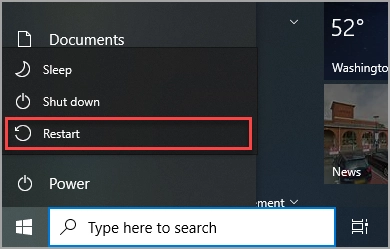
- Action: Restart your computer.
- Purpose: Rebooting clears the system’s memory and stops all running processes, including those that might be hanging or invisible in the background and still holding onto network connections. This refresh can reset the system’s network connection count.
Step 3: Log in to Your Computer
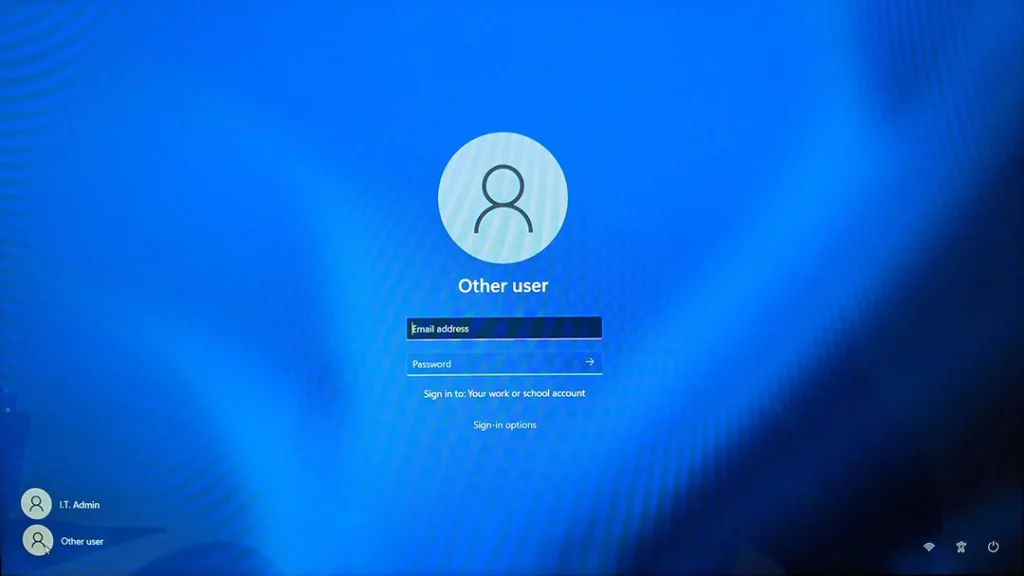
- Action: Power up and log into your computer without re-establishing a network connection.
- Purpose: Logging in without an active network connection ensures that no network processes start up automatically and occupy connection slots before you have a chance to reset the system fully.
Step 4: Reconnect to the Network
- Action: Once logged in and your desktop is loaded, reconnect your network cable or turn on your WiFi.
- Purpose: Reconnecting to the network after the system has fully started up ensures that all network services and applications initialize correctly and register their connections clearly. This helps the system manage connection limits more effectively and avoids ghost sessions that can consume connection slots invisibly.
Step 5: Check the Operating System’s Limitations
- Different Windows Versions and Connection Limits: Windows operating systems have varied limitations on the number of connections based on the edition. For example, Windows 10 Home allows fewer concurrent connections compared to Windows 10 Pro or Enterprise. Understanding your version’s limits is crucial to determining if an upgrade is necessary.
- Upgrading Options: If you frequently hit the connection limit, consider upgrading to a higher edition of Windows that supports more simultaneous connections. This can be especially important for server environments or businesses with many remote users. Microsoft offers straightforward paths for upgrading directly through the System Settings under “Update & Security.”
Step 6: Modify Group Policy Settings
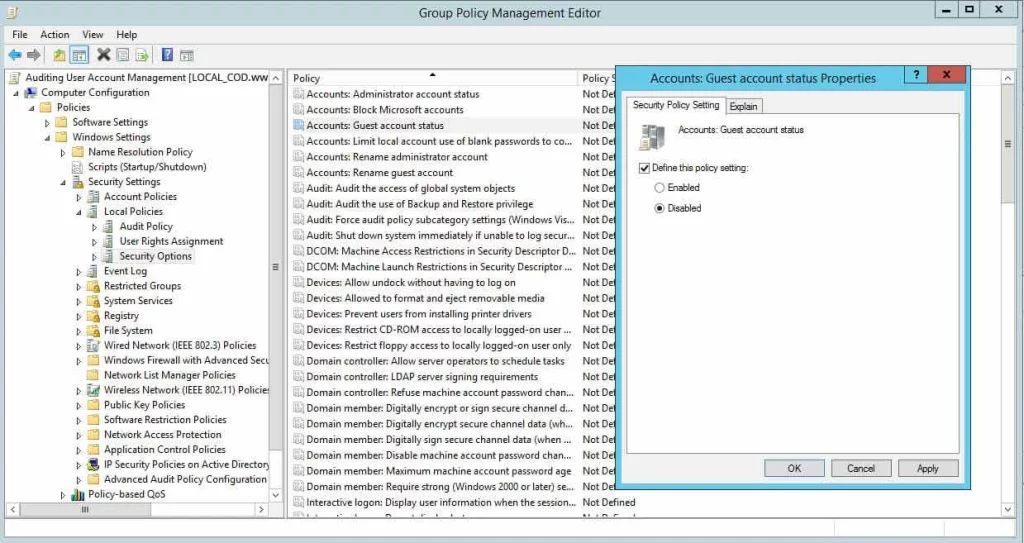
- Accessing Group Policy Editor: Press
Win + R, typegpedit.msc, and press Enter. This opens the Local Group Policy Editor. - Adjusting Network and Remote Access Policies: Navigate to
Computer Configuration>Administrative Templates>Network>Network Connections. Here, you can find settings that may influence connection limits, like limiting the number of simultaneous users on a Windows machine. Adjust these settings according to your needs, ensuring compliance with your organizational policies.
Step 7: Increase Connection Limits via Registry (Advanced)
- Warning About Editing the Registry: Modifying the Windows Registry can have significant implications. Always back up the registry before making changes.
- Step-by-Step Guide to Modifying Relevant Registry Keys:
- Open the Registry Editor by typing
regeditin the Run dialog (Win + R). - Navigate to
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\. - Locate the
fSingleSessionPerUserkey. Change the value from1(limit each user to one session) to0(allow multiple sessions per user). - Navigate to
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon\. - Find the
MaxConnectionsPerServerkey. If it does not exist, right-click, select New > DWORD (32-bit) Value, and name itMaxConnectionsPerServer. Set this value to a higher number to increase the limit of simultaneous connections. - Restart your computer for changes to take effect.
- Open the Registry Editor by typing
Step 8: Managing Active Sessions
- How to View and Disconnect Active Sessions:
- Use the Command Prompt or PowerShell to manage sessions. For instance, typing
query sessionorqwinstawill list active sessions. You can disconnect a session using thelogoffcommand followed by the session ID.
- Use the Command Prompt or PowerShell to manage sessions. For instance, typing
- Tools and Commands to Manage Connections:
- Remote Desktop Services Manager: Part of the Remote Server Administration Tools (RSAT), this tool allows administrators to see and manage all active RDP sessions and connections.
- Windows PowerShell: Scripts can be written to automate the viewing and disconnecting of sessions, especially useful in larger environments.
- Third-party software: Tools like TeamViewer or AnyDesk also provide built-in features to monitor and manage connections, offering more user-friendly interfaces and additional functionalities.
Related Post: How to Fix the “Cannot Create Key” Error Writing to the Registry
Additional Tips
- Check for Updates: Before attempting the steps, ensure your system and network drivers are up-to-date. Sometimes, connection issues are related to software bugs that are resolved in updates.
- Monitor Connection Usage: If the problem recurs, consider using network monitoring tools to see which applications or processes are using your network connections. This can help identify if a particular software is not releasing connections properly.
- Consult IT Support: If the issue persists, it may be worthwhile to consult with IT support or a network specialist. There could be deeper network configuration issues or hardware limitations at play.
This method is particularly useful for intermittent issues or when the error appears suddenly and is not a chronic problem. For environments where connection limits are frequently reached due to high user demand, more robust solutions involving network configuration or hardware upgrades might be necessary.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the cause of no Internet connection?
A: Common reasons why the internet is not working. There can be a number of reasons for having no internet, even when the Wi-Fi symbol shows that you’re connected. The most common cause is a problem with your router or modem, or a loose cable, but your internet can also fail because of a more technical reason.
How do you get an internet connection?
A: Choose an Internet Provider and acquire a modem and a router (sometimes these will come together in one device called a “wireless gateway”). Plug the modem into your wall jack and into a power outlet. Give it a few minutes to boot up. Then, if separate, connect your router and modem with an ethernet cable.
How do I fix connection loss?
A: Restart Your Modem/Router:
Whenever there’s a problem with your internet connection, the first thing you should do is restart your router. It could be you’re dealing with router overload. Be it slow upload speeds or the internet connection dropping.
How to solve network problems?
A: Check for local connectivity issues: The first step in troubleshooting network errors is to check cables, devices, switches, and routers for proper functioning. Teams can also try restarting devices such as the modem, PC, and router to resolve simple network issues.
What is a server connection issue?
A: “Connection to Server Failed” is a common error when your device cannot connect with a server. It can be due to various reasons, such as internet issues, server downtime, incorrect settings, or firewall restrictions.
Conclusion
The “The Number of Connections to This Computer Is Limited” error can be a significant hindrance in any network-dependent environment, be it a bustling corporate office or a remote educational facility. Addressing this issue is crucial not only for maintaining operational continuity but also for ensuring that all team members have reliable access to the necessary digital resources. Mismanaged connection settings can lead to productivity losses, frustrations, and even critical delays in workflows that depend on network access.







