Exploring the 5 Biggest Hacks of All Time
The digital world of today is complete with cybersecurity. As we increasingly turn to technology in almost every aspect of our personal and professional pursuits, the need to protect our digital assets has grown proportionately. Cybersecurity protects systems, networks, and programs against digital attacks. These attacks can lead to data compromise, operational paralysis, and substantial financial losses.
We live in a world of ever-evolving cyber threats where malicious actors never give up searching for vulnerabilities to exploit. No one is above cyber-attacks dangers, ranging from individual citizens and small businesses to large corporations. Cybersecurity breaches can have devastating outcomes that range from identity theft and financial losses to compromised national security and loss of human life.
As we launch into cybersecurity, we shall set the stage with an appreciation of the magnitude of threats we face. Looking through some of the most significant cyber-attacks ever, we shall derive fascinating insights and lessons that will help us better prepare for and mitigate such threats in the future.
Table of Contents
What are Cyber Hacks, and Why Do They Happen?
Cyber hacks, or cyber-attacks, are activities carried out intentionally to invade a computer system, network, or device without authority to retrieve data, causing disruption or destruction. Malware attacks, phishing, Distributed Denial-of-Service Attacks, and exploitation of software vulnerabilities mete them out.

Cyber hacks occur for a multitude of reasons, including:
- Financial gain: Cybercriminals often target financial institutions, businesses, and individuals to steal sensitive information, such as credit card numbers or banking credentials, for monetary gain.
- Espionage: Nation-states and hacker groups may use cyber espionage to steal trade secrets, intellectual property, or classified information for strategic advantages.
- Hacktivism: Some hackers are motivated by political or ideological beliefs and seek to disrupt or deface websites or systems to spread their message or cause disruption.
- Cyber warfare: In times of conflict, nations may resort to cyber attacks to disrupt their adversaries’ critical infrastructure, military operations, or communication systems.
- Personal motivations: Some hackers use cyber attacks for personal reasons, such as revenge, challenge, or simply demonstrating their skills.
Regardless of the motivation, cyber hacks can have far-reaching consequences, making it essential for individuals, businesses, and governments to prioritize cybersecurity and implement robust measures to protect their digital assets.
The Five Biggest Hacks Of All Time
Whereas cyber attacks occur daily, some have left an indelible mark on the cybersecurity landscape due to their scale, impact, and audacity. Let’s dive into five of the biggest hacks and what they have taught us.
Hack 1: The Virus That Destroyed Nuclear Equipment
In 2010, a sophisticated and highly targeted malware, Stuxnet, was discovered. This malicious code, believed to have been developed by the United States and Israel, was designed to infiltrate and sabotage Iran’s nuclear program by causing centrifuges to spin out of control and self-destruct.

Stuxnet was a game-changer in the world of cyber warfare, as it demonstrated malware’s ability to cause physical damage to critical infrastructure. The virus spread through infected USB drives and exploited vulnerabilities in Microsoft Windows, allowing it to gain control of industrial control systems used in nuclear facilities.
The impact of Stuxnet was significant, as it reportedly caused substantial damage to Iran’s nuclear program, delaying their efforts by several years. However, it also raised concerns about the potential for similar attacks on critical infrastructure worldwide, highlighting the need for enhanced cybersecurity measures.
Hack 2: The Bedroom Hacker Who Made an Entire US Armory Disappear
In 2008, a young hacker named Gary McKinnon, operating from his bedroom in London, managed to infiltrate and gain access to numerous computer systems belonging to NASA, the United States Department of Defense, and various military installations.

McKinnon’s motivation was to search for evidence of extraterrestrial life and free energy suppression, but his actions caused significant disruptions and exposed vulnerabilities in the cybersecurity defenses of some of the world’s most sensitive networks.
It is alleged that, in his hacking spree, McKinnon deleted critical system files that made the networks inoperable and had access to sensitive data, including those relating to the running of the International Space Station. The dispute over his extradition to the United States from the United Kingdom has been rather long-drawn, underlining the international dimension of cyber threat issues and the requirement for global coordination in combating them.
Hack 3: The First Cyber War
In 2007, a series of coordinated cyber-attacks targeted various government and private organizations in Estonia, causing widespread disruptions and effectively crippling the country’s digital infrastructure.

The attacks, believed to have been orchestrated by Russian hackers in retaliation for the relocation of a Soviet-era memorial, involved:
- Distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks.
- Website defacements.
- The exploitation of vulnerabilities in various systems.
This incident, known as the “Cyber War in Estonia,” was one of the first large-scale cyber attacks against a nation-state and oriented the contemporary world to the weakness of modern societies against cyber threats. It led NATO to open the Cooperative Cyber Defence Centre of Excellence (CCDCOE) in Estonia, aimed at enhancing cybersecurity and international cooperation capabilities.
Hack 4: Bitcoin’s Black Monday
In 2014, Mt. Gox, the world’s largest Bitcoin exchange at the time, suffered a devastating hack that led to the loss of approximately 850,000 Bitcoins, valued at around $450 million at the time.

Hackers could siphon off Bitcoins for a prolonged period by taking advantage of the vulnerabilities in the exchange’s software and security measures, causing significant financial losses for Mt. Gox and its customers and hitting the credibility and public perception of Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies.
The Mt. Gox hack pointed out that digital currencies were a fast-moving space that demanded robust security measures and the risks involved with centralized exchanges. It also drew closer scrutiny into cryptocurrency platforms for increased regulation and turned a refocused interest in secure decentralized alternatives.
Hack 5: PlayStation Network 2011 Hack
In 2011, the hacking group LulzSec—the five defendants—”wreaked havoc on the Internet,” according to an FBI news release, after being accused of hacking several organizations, including Sony Pictures Entertainment.
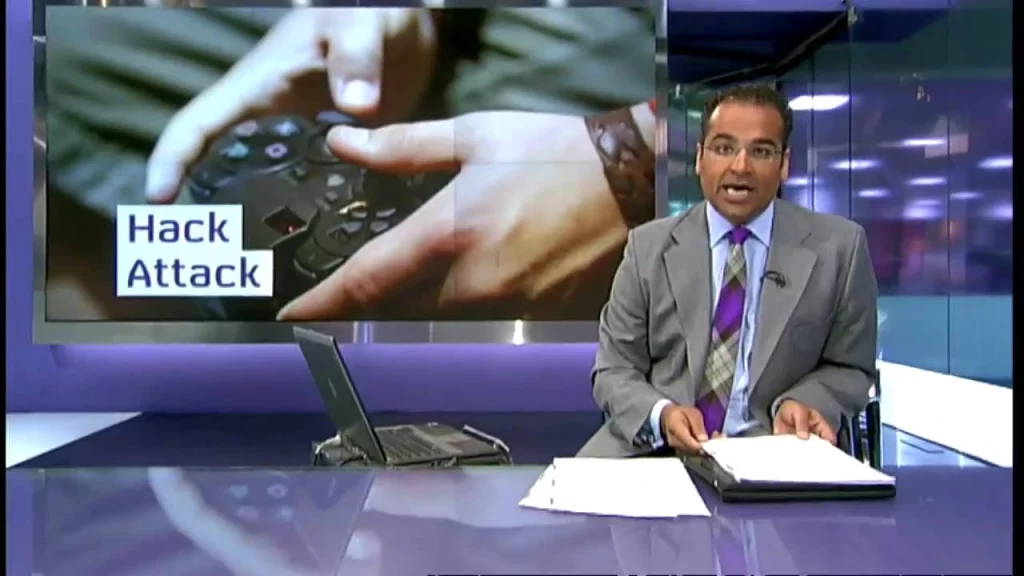
Indeed, cyber attacks have ranged from simple website defacement and publishing of customer data to actual theft of intellectual property, as was the case with Sony. In that case of the attack, sensitive data, including the personal information of millions of customers and the source code of various Sony products, had been stolen. These hackers could further deface the website and leak confidential information, leading to a lot of reputational and financial damage to the company.
Sony estimated the breach cost to be some $171 million, including expenditure on legal fees, identity theft protection services, and mending of IT systems. The attacks by LulzSec have illustrated the vulnerability of massive corporations to cyber threats and how those threats can carry over into actual financial costs and harm the company’s reputation.
Related Post: How to Track a Scammer on WhatsApp
Lessons Learned from these Significant Hacks
While these hacks have had devastating impacts, they have also served as valuable lessons for individuals, businesses, and governments. Here are some key takeaways:
- Cybersecurity is a continuous process: Cybersecurity is not a one-time effort but an ongoing process that requires constant vigilance, updating, and adaptation to new threats.
- Prioritize security measures: Robust security measures, including strong encryption, multi-factor authentication, and regular software updates, are crucial in mitigating cyber threats.
- Educate and train personnel: Employees and personnel should receive regular cybersecurity training to raise awareness about potential threats and best practices for protecting sensitive information.
- Collaborate and share information: Effective cybersecurity requires collaboration and information sharing among organizations, industries, and nations to identify and respond to emerging threats.
- Invest in cybersecurity: Cybersecurity should be an organization’s top priority, and adequate resources should be allocated to implement and maintain effective security measures.
- Prepare for the worst: Organizations should have comprehensive incident response plans to mitigate cyber-attacks impact and facilitate recovery efforts.
- Embrace innovation: As cyber threats evolve, organizations must continually innovate and adopt new technologies and strategies to stay ahead of malicious actors.
The Impact of Cybersecurity Breaches on Businesses and Individuals
Cybersecurity breaches can have far-reaching consequences for both businesses and individuals. For businesses, the financial implications can be staggering, including:
- Direct financial losses: Cyber attacks can result in the theft of funds, intellectual property, or sensitive data, leading to significant economic losses.
- Operational disruptions: Cyber attacks can disrupt business operations, causing downtime, lost productivity, and potential revenue losses.
- Reputational damage: High-profile cyber attacks can severely damage a company’s reputation, eroding customer trust and potentially leading to long-term financial consequences.
- Legal and regulatory penalties: Businesses may face legal action, fines, and penalties for failing to protect customer data or comply adequately with cybersecurity regulations.
For individuals, the impact of cybersecurity breaches can be equally devastating:
- Identity theft: Cyber criminals can steal personal information, such as Social Security numbers, credit card details, and banking credentials, leading to identity theft and financial losses.
- Privacy violations: Cyber attacks can compromise sensitive personal data, including medical records, communication logs, and private photographs or videos, resulting in significant emotional distress and potential legal consequences.
- Financial losses: Individuals can suffer direct financial losses due to fraudulent transactions, unauthorized access to bank accounts, or extortion attempts.
- Reputational damage: In some cases, cybersecurity breaches can lead to the public disclosure of sensitive or embarrassing information, damaging an individual’s reputation and personal relationships.
Protecting against these consequences underscores the critical importance of robust cybersecurity measures for businesses and individuals.
How to Protect Yourself and your Business from Cyber Threats
In the face of ever-evolving cyber threats, it is essential to implement comprehensive cybersecurity measures to safeguard your digital assets. Here are some effective strategies to protect yourself and your business:
- Implement strong access controls: Secure your accounts and systems by using multi-factor authentication, strong passwords, and regular password updates.
- Keep software and systems up-to-date: Regularly update your operating systems, applications, and security software to address known vulnerabilities and patch security holes.
- Educate and train personnel: Provide regular cybersecurity training to employees, emphasizing best practices for identifying and mitigating potential threats, such as phishing attempts and social engineering attacks.
- Backup data regularly: Implement a robust data backup strategy to ensure critical data can be recovered during a cyber attack or system failure.
- Use encryption: Encrypt sensitive data in transit and at rest to protect it from unauthorized access.
- Implement firewalls and intrusion detection systems: Deploy firewalls and intrusion detection systems to monitor and control network traffic, detecting and preventing potential cyber threats.
- Conduct regular security audits: Regularly assess your cybersecurity posture by conducting security audits and penetration testing to identify and address vulnerabilities.
- Develop an incident response plan: Establish a comprehensive incident response plan to mitigate the cyber-attack’s impact and facilitate swift recovery efforts.
- Leverage cybersecurity services: Consider partnering with reputable cybersecurity firms or managed security service providers to augment your in-house capabilities and stay ahead of emerging threats.
- Stay informed and vigilant: Follow reputable sources and industry experts by following the latest cybersecurity trends, threats, and best practices.
Implementing these strategies can significantly reduce your risk of being a victim of cyber attacks and protect your digital assets from potential threats.
Conclusion
With the rapidly evolving digital world, cybersecurity will always be an issue at the heart of being for people, corporations, and governments. Thus, These hacks provide us with evidence of how devastating a poor cyber security measure was; for this reason, someone should be very keen.
The future of cybersecurity, quite understandably, will thus be driven by the development of sophisticated technologies—artificial intelligence, machine learning, quantum computing—to address the ever-evolving threat landscape. However, this requires an all-out commitment by all players; prime importance should be accorded to cybersecurity, effective measures should be implemented, and collaboration and sharing of information should be encouraged.